Plasmodium microtubule-binding protein EB1 is critical for partitioning of nuclei in male gametogenesis
- PMID: 37535401
- PMCID: PMC10470552
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.00822-23
Plasmodium microtubule-binding protein EB1 is critical for partitioning of nuclei in male gametogenesis
Abstract
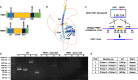
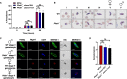
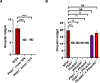
Sexual reproduction of the malaria parasites is critical for their transmission to a mosquito vector. Several signaling molecules, such as kinases and phosphatases, are known to regulate this process. We previously demonstrated that Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) Ca2+-dependent protein kinase 4 (CDPK4) and serine/arginine-rich protein kinase 1 (SRPK1) are critical for axoneme formation during male gametogenesis, with genetic deletion of either gene causing a complete block in parasite transmission to the mosquito. A comparative phospho-proteome analysis of Pfcdpk4- and RNA-seq analysis of Pfsrpk1- gametocytes showed that these kinases regulate similar biological processes linked to both microtubule (MT) dynamics and cell motility. One of these proteins was a nuclear MT-associated
Keywords: Plasmodium; gamete; microtubules; mosquito; nucleus; transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
