Peptide barcode of multidrug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated from patients in Thailand
- PMID: 37535640
- PMCID: PMC10399818
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289308
Peptide barcode of multidrug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated from patients in Thailand
Abstract
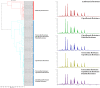
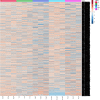
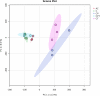
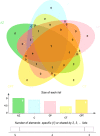
The emergence of multidrug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae constitutes a serious threat to public health. The present study aimed to investigate peptidome-based biomarkers of multidrug-resistant N. gonorrhoeae, using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS). The peptide barcode database of multidrug resistant N. gonorrhoeae was generated from the whole-cell peptides of 93 N. gonorrhoeae isolated from patients in Thailand. The dendrogram of 93 independent isolates of antibiotic-resistant N. gonorrhoeae revealed five distinct clusters including azithromycin resistance group (AZ), ciprofloxacin resistance group (C), ciprofloxacin and penicillin resistance group (CP), ciprofloxacin and tetracycline resistance group (CT), ciprofloxacin, penicillin and tetracycline resistance group (CPT). The peptidomes of all clusters were comparatively analyzed using a high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method (LC-MS). Nine peptides derived from 9 proteins were highly expressed in AZ (p value < 0.05). These peptides also played a crucial role in numerous pathways and showed a strong relationship with the antibiotic resistances. In conclusion, this study showed a rapid screening of antibiotic-resistant N. gonorrhoeae using MALDI-TOF MS. Additionally, potential specific peptidome-based biomarker candidates for AZ, C, CP, CT and CPT-resistant N. gonorrhoeae were identified.
Copyright: © 2023 Roytrakul et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Report on global sexually transmitted infection surveillance, 2018. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/277258/9789241565691-en... Accessed on 12 December 2022.
-
- Bureau of Epidemiology Department of Disease Control. Ministry of Public Health Nonthaburi THAILAND. Thailand National Disease Surveillance Report. Available online: http://doe.moph.go.th/surdata/disease.php?ds=37 Accessed on 12 December 2022.
-
- Buder S, Dudareva S, Jansen K, Loenenbach A, Nikisins S, Sailer A, et al.. GORENET study group. Antimicrobial resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Germany: low levels of cephalosporin resistance, but high azithromycin resistance. BMC Infect Dis. 2018; 18(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-2944-9 ; PMCID: PMC5772720. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sirivongrangson P, Girdthep N, Sukwicha W, Buasakul P, Tongtoyai J, Weston E, et al. EGASP Thailand Workgroup. The first year of the global Enhanced Gonococcal Antimicrobial Surveillance Programme (EGASP) in Bangkok, Thailand, 2015–2016. PLoS One. 2018; 13(11):e0206419. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206419 ; PMCID: PMC6226150. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

