Serological survey to estimate SARS-CoV-2 infection and antibody seroprevalence at a large public university: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37536960
- PMCID: PMC10401225
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-072627
Serological survey to estimate SARS-CoV-2 infection and antibody seroprevalence at a large public university: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated the seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies among adults over 18 years.
Design: Prospective cohort study.
Settings: A large public university.
Participants: This study took volunteers over 5 days and recruited 1064 adult participants.
Primary outcome measures: Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies due to previous exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and/or vaccination.
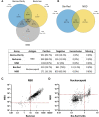
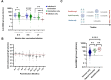
Results: The seroprevalence of the antireceptor binding domain (RBD) antibody was 90% by a lateral flow assay and 88% by a semiquantitative chemiluminescent immunoassay. The seroprevalence for antinucleocapsid was 20%. In addition, individuals with previous natural COVID-19 infection plus vaccination had higher anti-RBD antibody levels compared with those who had vaccination only or infection only. Individuals who had a breakthrough infection had the highest anti-RBD antibody levels.
Conclusion: Accurate estimates of the cumulative incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection can inform the development of university risk mitigation protocols such as encouraging booster shots, extending mask mandates or reverting to online classes. It could help us to have clear guidance to act at the first sign of the next surge as well, especially since there is a surge of COVID-19 subvariant infections.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemiology; SARS-CoV-2.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- CDC . COVID data Tracker. Available: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker [Accessed 12 Jan 2023].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
