Providing open imaging data at scale: An EMBL-EBI perspective
- PMID: 37537341
- PMCID: PMC10492673
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-023-02216-2
Providing open imaging data at scale: An EMBL-EBI perspective
Abstract
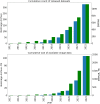
Biological imaging is one of the primary tools by which we understand living systems across scales from atoms to organisms. Rapid advances in imaging technology have increased both the spatial and temporal resolutions at which we examine those systems, as well as enabling visualisation of larger tissue volumes. These advances have huge potential but also generate ever increasing amounts of imaging data that must be stored and analysed. Public image repositories provide a critical scientific service through open data provision, supporting reproducibility of scientific results, access to reference imaging datasets and reuse of data for new scientific discovery and acceleration of image analysis methods development. The scale and scope of imaging data provides both challenges and opportunities for open sharing of image data. In this article, we provide a perspective influenced by decades of provision of open data resources for biological information, suggesting areas to focus on and a path towards global interoperability.
Keywords: Bioimaging; Data integration; Data management; Metadata.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Brazma A, Ball C, Bumgarner R, et al. MINSEQE: minimum information about a high-throughput nucleotide sequencing experiment – a proposal for standards in functional genomic data reporting. Zenodo. 2012 doi: 10.5281/zenodo.5706412. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

