Real-world effectiveness, satisfaction, and optimization of ubrogepant for the acute treatment of migraine in combination with onabotulinumtoxinA: results from the COURAGE Study
- PMID: 37537578
- PMCID: PMC10399003
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-023-01622-0
Real-world effectiveness, satisfaction, and optimization of ubrogepant for the acute treatment of migraine in combination with onabotulinumtoxinA: results from the COURAGE Study
Abstract
Background: Individuals using onabotulinumtoxinA as a preventive migraine treatment often use acute treatments for breakthrough attacks. Data on real-world effectiveness of the small-molecule calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist ubrogepant in combination with onabotulinumtoxinA are limited.
Methods: COURAGE, a prospective, multiple attack, observational study, evaluated the real-world effectiveness of ubrogepant (50 or 100 mg) for acute treatment of migraine in people receiving onabotulinumtoxinA, an anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody (mAb), or both. This analysis focused only on onabotulinumtoxinA users. The Migraine Buddy app was used to identify eligible participants and track response to treated attacks. For each ubrogepant-treated attack, meaningful pain relief (MPR) and return to normal function (RNF) at 2 and 4 h post-dose over 30 days was assessed. MPR was defined as a level of relief that is meaningful to the participant, usually occurring before the pain is all gone. After 30 days, satisfaction was reported on a 7-point scale and overall acute treatment optimization was evaluated using the migraine Treatment Optimization Questionnaire-4 (mTOQ-4).
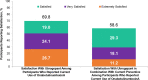
Results: This analysis included 122 participants who received ubrogepant and onabotulinumtoxinA and reported on 599 ubrogepant-treated attacks. Following the first ubrogepant-treated attack, MPR was achieved in 53.3% of participants 2 h post-dose and in 76.2% of participants 4 h post-dose. RNF was achieved in 25.4% of participants 2 h post-dose and in 45.9% of participants 4 h post-dose. MPR and RNF results were similar across up to 10 ubrogepant-treated attacks. After 30 days, satisfaction with ubrogepant in combination with onabotulinumtoxinA was reported by 69.8% of participants and acute treatment optimization (defined as mTOQ-4 score ≥ 4) was achieved in 77.6%.
Conclusions: In this prospective real-world effectiveness study, ubrogepant treatment in onabotulinumtoxinA users with self-identified migraine was associated with high rates of MPR and RNF at 2 and 4 h as well as satisfaction and acute treatment optimization. Although the lack of a contemporaneous control group limits causal inference, these findings demonstrate the feasibility of using a novel, app-based design to evaluate the real-world effectiveness and satisfaction of treatments.
Keywords: Chronic migraine; OnabotulinumtoxinA; Ubrogepant.
© 2023. Springer-Verlag Italia S.r.l., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
RBL has received research support from the National Institutes of Health, the FDA, and the National Headache Foundation. He serves as consultant, advisory board member, or has received honoraria or research support from AbbVie/Allergan, Amgen, Biohaven, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories (Promius), electroCore, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Lundbeck, Merck, Novartis, Teva, Vector, and Vedanta Research. He receives royalties from
EE, NDA, and DS were employees of OPEN Health Group at the time of study conduct.
LD serves as a consultant, advisory board member, or has received honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Teva.
AMA, JC-DL, and KS are employees of AbbVie and may hold AbbVie stock.
SH serves as a consultant, advisory board member, or has received honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Currax, Eli Lilly, Impel, Lundbeck, Novartis, Teva, Theranica, and Upsher-Smith.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Real-World Use of Ubrogepant as Acute Treatment for Migraine with an Anti-Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibody: Results from COURAGE.Neurol Ther. 2024 Feb;13(1):69-83. doi: 10.1007/s40120-023-00556-8. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Neurol Ther. 2024. PMID: 37910303 Free PMC article.
-
Ubrogepant users' real-world experience: Patients on ubrogepant, characteristics and outcomes (UNIVERSE) study.Headache. 2024 Nov-Dec;64(10):1244-1252. doi: 10.1111/head.14839. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Headache. 2024. PMID: 39324611
-
Real-world efficacy, tolerability, and safety of ubrogepant.Headache. 2021 Apr;61(4):620-627. doi: 10.1111/head.14062. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Headache. 2021. PMID: 33547676
-
Real-World Evidence for Control of Chronic Migraine Patients Receiving CGRP Monoclonal Antibody Therapy Added to OnabotulinumtoxinA: A Retrospective Chart Review.Pain Ther. 2021 Dec;10(2):809-826. doi: 10.1007/s40122-021-00264-x. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Pain Ther. 2021. PMID: 33880725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pooled Analysis of Real-World Evidence Supports Anti-CGRP mAbs and OnabotulinumtoxinA Combined Trial in Chronic Migraine.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Aug 1;14(8):529. doi: 10.3390/toxins14080529. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36006191 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Combining treatments for migraine prophylaxis: the state-of-the-art.J Headache Pain. 2024 Dec 5;25(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01925-w. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39639191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gepants: Key Features of A Potent Therapeutic Option and Considerations in The Latin American Context.Rev Neurol. 2025 Jun 25;80(5):38637. doi: 10.31083/RN38637. Rev Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40613410 Free PMC article. Review. English.
-
Gepants in Primary Care: A Targeted Approach to Acute and Preventive Treatment of Migraine.Pain Ther. 2025 Aug;14(4):1263-1278. doi: 10.1007/s40122-025-00757-z. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Pain Ther. 2025. PMID: 40579665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-World Evidence of the Safety and Effectiveness of Atogepant Added to OnabotulinumtoxinA for the Preventive Treatment of Chronic Migraine: A Retrospective Chart Review.Pain Ther. 2024 Dec;13(6):1571-1587. doi: 10.1007/s40122-024-00649-8. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Pain Ther. 2024. PMID: 39287781 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Migraine Head Pain and Botulinum Toxin.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Oct 9;16(10):431. doi: 10.3390/toxins16100431. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39453207 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steiner TJ, Jensen R, Katsarava Z, Linde M, MacGregor EA, Osipova V, et al. Aids to management of headache disorders in primary care (2nd edition): on behalf of the European Headache Federation and Lifting the Burden: the Global Campaign against Headache. J Headache Pain. 2019;20:57. doi: 10.1186/s10194-018-0899-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

