Natto: A medicinal and edible food with health function
- PMID: 37538862
- PMCID: PMC10394349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chmed.2023.02.005
Natto: A medicinal and edible food with health function
Abstract
Natto is a soybean product fermented by natto bacteria. It is rich in a variety of amino acids, vitamins, proteins and active enzymes. It has a number of biological activities, such as thrombolysis, prevention of osteoporosis, antibacterial, anticancer, antioxidant and so on. It is widely used in medicine, health-care food, biocatalysis and other fields. Natto is rich in many pharmacological active substances and has significant medicinal research value. This paper summarizes the pharmacological activities and applications of natto in and outside China, so as to provide references for further research and development of natto.
Keywords: active ingredients; application of natto; mechanisms of action; natto; pharmacological actions.
© 2023 Tianjin Press of Chinese Herbal Medicines. Published by ELSEVIER B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
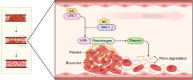
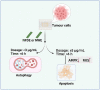


References
-
- An X.F., Liu H.R., Dai X.M., Zhang B. Effect of natto lipopeptide on human breast cancer mcf-7 cells. Science and Technology of Food Industry. 2014;35(3):343–350.
-
- Azimirad M., Alebouyeh M., Naji T. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin 8 in human adenocarcinoma cell line HT-29 by spore probiotics: B. coagulans and B. subtilis (natto). Probiotics and Antimicrobial. Proteins. 2017;9(1):56–63. - PubMed
-
- Bao K., Chen T.L., Zhang S., Huang Z.Z., Ding Q.Q. A succinyl isoflavone identified in natto promotes anti-ischemic effects in the middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. Journal of Functional Foods. 2020;73(2020)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

