The cross-linguistic comparison of perceptual strength norms for Korean, English and L2 English
- PMID: 37538997
- PMCID: PMC10395129
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1188909
The cross-linguistic comparison of perceptual strength norms for Korean, English and L2 English
Abstract
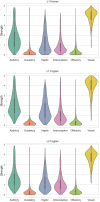
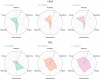
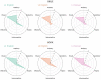
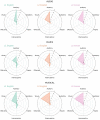
This study aimed to establish perceptual strength norms for 1,000 words in the languages of Korean, English, and L2 English, in order to investigate the similarity and difference across languages as well as the influence of the environment on semantic processing. The perceptual strength norms, which are a collection of word profiles that summarize how a word is experienced through different sensory modalities including the five common senses and interoception, provide a valuable tool for testing embodiment cognition theory. The results of this study demonstrated that language users had parallel sensory experiences with concepts, and that L2 learners were also able to associate their sensory experiences with linguistic concepts. Additionally, the results highlighted the importance of incorporating interoception as a sensory modality in the development of perceptual strength norms, as it had a negative correlation with both vision and concreteness. This study was the first to establish norms for Korean and L2 English and directly compare languages using the identical and translation-equivalent word list.
Keywords: abstract concept; conceptualization; cross-linguistic; embodiment cognition; grounded cognition; interoception; perceptual strength; second language processing.
Copyright © 2023 Lee and Shin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Barros-Loscertales A., González J., Pulvermüller F., Ventura-Campos N., Bustamante J. C., Costumero V., et al. (2012). Reading salt activates gustatory brain regions: fMRI evidence for semantic grounding in a novel sensory modality. Cerebral Cortex 22, 2554–2563. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhr324 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B., Walker S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 67, 1–48. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1406.5823 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

