Pharmacological effects and mechanism of Kaihoujian Throat Spray (children's type) in the treatment of pediatric acute pharyngitis and tonsillitis
- PMID: 37539230
- PMCID: PMC10395134
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17802
Pharmacological effects and mechanism of Kaihoujian Throat Spray (children's type) in the treatment of pediatric acute pharyngitis and tonsillitis
Abstract
Context: Kaihoujian Throat Spray children's type (KHJSC) is a Chinese medicine prescription for treating pediatric acute pharyngitis and tonsillitis (APT). However, its relevant mechanisms remain unclear.
Objective: To investigate the pharmacological effects of KHJSC on APT in vitro and in vivo, and explore the possible mechanism and target proteins.
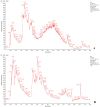
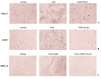
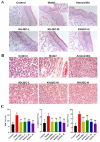
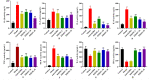
Materials and methods: The antiviral and antibacterial effects in vitro were evaluated by IC50 and MICs. Thirty-six Japanese white rabbits were averagely divided into control group, model group, amoxicillin group and 3 dose groups of KHJSC (720, 540 and 360 μL/kg/d). The model rabbits were injected with β-hemolytic Streptococcus solution into the tonsils for 2 consecutive days. KHJSC treatment started on the third day. The whole blood, serum, tonsil tissues and pharyngeal mucosa tissues were collected for routine blood tests, proteomic, ELISA and other tests on the sixth day.
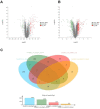
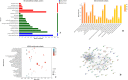
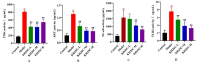
Results: The IC50 of KHJSC on HCoV-229E, influenza PR8 and Ad3 were 1.99, 1.99 and 4.49 mg/mL, respectively; MICs of MDR-PA, MRSA and β-hemolytic Streptococcus were 350, 350, and 175 mg/mL. KHJSC markedly decreased the number of white blood cells, lymphocytes, neutrophils, and the level of IL-1β, IL-5, IL-6, IL-18, TNF-α and MCP-1; increased the content of IL-2 and IFN-γ. Proteomic analysis and ELISA revealed that PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, NF-κB signaling pathway and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway were the potential mechanisms of KHJSC against APT.
Discussion and conclusion: These results provided the reference and scientific basis for the application of KHJSC in clinic and further mechanisms study.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Antiviral; TMT quantitative proteomic; Traditional Chinese medicine; β-hemolytic Streptococcus.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation on immediate analgesic efficacy and safety of Kai-Hou-Jian spray (children's type) in treating sore throat caused by acute pharyngitis and tonsillitis in children: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Mar 18;22(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05148-1. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33736674 Free PMC article.
-
Liu Shen Wan inhibits influenza a virus and excessive virus-induced inflammatory response via suppression of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 24;252:112584. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112584. Epub 2020 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31972325
-
Network Pharmacology Analysis of the Mechanisms of Compound Herba Sarcandrae (Fufang Zhongjiefeng) Aerosol in Chronic Pharyngitis Treatment.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Jun 28;15:2783-2803. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S304708. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34234411 Free PMC article.
-
Group C beta hemolytic Streptococci as a potential pathogen in patients presenting with an uncomplicated acute sore throat - a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.Scand J Prim Health Care. 2020 Jun;38(2):226-237. doi: 10.1080/02813432.2020.1753374. Epub 2020 May 2. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2020. PMID: 32362178 Free PMC article.
-
[Tonsillitis and sore throat in childhood].Laryngorhinootologie. 2014 Mar;93 Suppl 1:S84-102. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1363210. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Laryngorhinootologie. 2014. PMID: 24710788 Review. German.
Cited by
-
A review on the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicity of sophocarpine.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 29;15:1353234. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1353234. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38746009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tinosporae Radix attenuates acute pharyngitis by regulating glycerophospholipid metabolism and inflammatory responses through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 6;15:1491321. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1491321. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39568590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ma Y.N., Zhong C.L., Hu S.Y., Cai Q.H., Guo S.X. Evaluation on immediate analgesic efficacy and safety of Kai-Hou-Jian spray (children's type) in treating sore throat caused by acute pharyngitis and tonsillitis in children: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2021;22:216. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pavez D., Pérez R., Cofré J., Rodríguez J. Recommendations for diagnosis and etiological treatment of acute streptococcal pharyngotonsilitis in pediatrics. Rev Chilena Infectol. 2019;36:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Espadas Macia D., Flor Macian E.M., Borras R., Poujois Gisbert S., Munoz Bonet J.I. Streptococcus pyogenes infection in paediatrics: from pharyngotonsillitis to invasive infections. Anales de pediatria. 2018;88:75–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

