A Case Report of Rare and Lethal Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Peritonitis in Infancy
- PMID: 37539401
- PMCID: PMC10394718
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.41303
A Case Report of Rare and Lethal Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Peritonitis in Infancy
Abstract
Peritoneal inflammation without a discernible intraperitoneal source is referred to as primary peritonitis. Only 2% of pediatric acute abdominal crises are diagnosed preoperatively. Association with other infections is uncommon and is often limited to hepatic and urinary pathogens. Here, we describe a case of primary peritonitis in a one-month-old child who had laparotomy and appendicectomy as per the recommended treatment plan. There were no accompanying hepatic and urinary diseases. In this instance, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was the responsible bacteria. The use of linezolid, as per the culture sensitivity report of intraperitoneal pus, ensured a smooth recovery in this case.
Keywords: acute abdominal emergencies; appendicectomy; methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (mrsa); perforation peritonitis; primary peritonitis.
Copyright © 2023, Kumar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

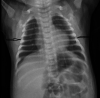
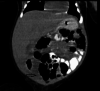
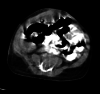

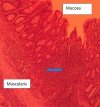
References
-
- Peritonitis in children with nephrotic syndrome. Gorensek MJ, Lebel MH, Nelson JD. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3368284/ Pediatrics. 1988;81:849–856. - PubMed
-
- Primary peritonitis: changing aspects 1956-1970. Fowler R. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5093237/ Aust Paediatr J. 1971;7:73–83. - PubMed
-
- Primary peritonitis in the newborn: a recently recognised disease. Lainakis N, Koulopoulos K, Kourakos A, Kostopoulos E, Trigas B, Skanavis K, Trapalis B. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19537122/ Ann Ital Chir. 2009;80:39–41. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
