Ionmob: a Python package for prediction of peptide collisional cross-section values
- PMID: 37540201
- PMCID: PMC10521631
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad486
Ionmob: a Python package for prediction of peptide collisional cross-section values
Abstract
Motivation: Including ion mobility separation (IMS) into mass spectrometry proteomics experiments is useful to improve coverage and throughput. Many IMS devices enable linking experimentally derived mobility of an ion to its collisional cross-section (CCS), a highly reproducible physicochemical property dependent on the ion's mass, charge and conformation in the gas phase. Thus, known peptide ion mobilities can be used to tailor acquisition methods or to refine database search results. The large space of potential peptide sequences, driven also by posttranslational modifications of amino acids, motivates an in silico predictor for peptide CCS. Recent studies explored the general performance of varying machine-learning techniques, however, the workflow engineering part was of secondary importance. For the sake of applicability, such a tool should be generic, data driven, and offer the possibility to be easily adapted to individual workflows for experimental design and data processing.
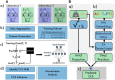
Results: We created ionmob, a Python-based framework for data preparation, training, and prediction of collisional cross-section values of peptides. It is easily customizable and includes a set of pretrained, ready-to-use models and preprocessing routines for training and inference. Using a set of ≈21 000 unique phosphorylated peptides and ≈17 000 MHC ligand sequences and charge state pairs, we expand upon the space of peptides that can be integrated into CCS prediction. Lastly, we investigate the applicability of in silico predicted CCS to increase confidence in identified peptides by applying methods of re-scoring and demonstrate that predicted CCS values complement existing predictors for that task.
Availability and implementation: The Python package is available at github: https://github.com/theGreatHerrLebert/ionmob.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P. et al. Tensorflow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. 2016.
-
- Bush MF, Campuzano IDG, Robinson CV.. Ion mobility mass spectrometry of peptide ions: effects of drift gas and calibration strategies. Anal Chem 2012;84:7124–30. - PubMed
-
- Chang CH, Yeung D, Spicer V. et al. Sequence-specific model for predicting peptide collision cross section values in proteomic ion mobility spectrometry. J Proteome Re 2021;20:3600–10. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y-W, Lin C-J. Feature ranking using linear svm. In: Guyon I, Aliferis C, Cooper G, Elisseeff A, Pellet J-P, Spirtes P, and Statnikov A (eds.), Proceedings of the Workshop on the Causation and Prediction Challenge at WCCI 2008, volume 3 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, 53–64. Hong Kong: PMLR, 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

