Neoantigen Targetability in Progressive Advanced Melanoma
- PMID: 37540567
- PMCID: PMC10570682
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1106
Neoantigen Targetability in Progressive Advanced Melanoma
Abstract
Purpose: The availability of (neo)antigens and the infiltration of tumors by (neo)antigen-specific T cells are crucial factors in cancer immunotherapy. In this study, we aimed to investigate the targetability of (neo)antigens in advanced progessive melanoma and explore the potential for continued T-cell-based immunotherapy.
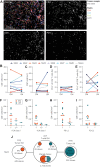
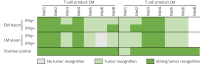
Experimental design: We examined a cohort of eight patients with melanoma who had sequential metastases resected at early and later time points. Antigen-presenting capacity was assessed using IHC and flow cytometry. T-cell infiltration was quantified through multiplex immunofluorescence. Whole-exome and RNA sequencing were conducted to identify neoantigens and assess the expression of neoantigens and tumor-associated antigens. Mass spectrometry was used to evaluate antigen presentation. Tumor recognition by autologous T cells was assessed by coculture assays with cell lines derived from the metastatic lesions.
Results: We observed similar T-cell infiltration in paired early and later metastatic (LM) lesions. Although elements of the antigen-presenting machinery were affected in some LM lesions, both the early and later metastasis-derived cell lines were recognized by autologous T cells. At the genomic level, the (neo)antigen landscape was dynamic, but the (neo)antigen load was stable between paired lesions.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that subsequently isolated tumors from patients with late-stage melanoma retain sufficient antigen-presenting capacity, T-cell infiltration, and a stable (neo)antigen load, allowing recognition of tumor cells by T cells. This indicates a continuous availability of T-cell targets in metastases occurring at different time points and supports further exploration of (neo)antigen-specific T-cell-based therapeutic approaches for advanced melanoma.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

References
-
- Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob JJ, Rutkowski P, Lao CD, et al. Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 2019;381:1535–46. - PubMed
-
- Serra-Bellver P, Versluis JM, Oberoi HK, Zhou C, Slattery TD, Khan Y, et al. Real-world outcomes with ipilimumab and nivolumab in advanced melanoma: a multicentre retrospective study. Eur J Cancer 2022;176:121–32. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

