Monomerization of TDP-43 is a key determinant for inducing TDP-43 pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 37540751
- PMCID: PMC10403219
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adf6895
Monomerization of TDP-43 is a key determinant for inducing TDP-43 pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
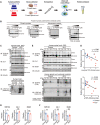
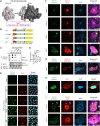
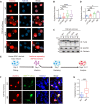
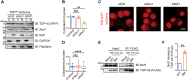
The cytoplasmic aggregation of TAR DNA binding protein-43 (TDP-43), also known as TDP-43 pathology, is the pathological hallmark of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). However, the mechanism underlying TDP-43 cytoplasmic mislocalization and subsequent aggregation remains unclear. Here, we show that TDP-43 dimerization/multimerization is impaired in the postmortem brains and spinal cords of patients with sporadic ALS and that N-terminal dimerization-deficient TDP-43 consists of pathological inclusion bodies in ALS motor neurons. Expression of N-terminal dimerization-deficient mutant TDP-43 in Neuro2a cells and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motor neurons recapitulates TDP-43 pathology, such as Nxf1-dependent cytoplasmic mislocalization and aggregate formation, which induces seeding effects. Furthermore, TDP-DiLuc, a bimolecular luminescence complementation reporter assay, could detect decreased N-terminal dimerization of TDP-43 before TDP-43 pathological changes caused by the transcription inhibition linked to aberrant RNA metabolism in ALS. These findings identified TDP-43 monomerization as a critical determinant inducing TDP-43 pathology in ALS.
Figures


Comment in
-
New mechanistic insights into TDP-43 pathology.Nat Rev Neurol. 2023 Oct;19(10):574. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00870-7. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37608120 No abstract available.
References
-
- P. Tziortzouda, L. Van Den Bosch, F. Hirth, Triad of TDP43 control in neurodegeneration: Autoregulation, localization and aggregation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 22, 197–208 (2021). - PubMed
-
- T. Arai, M. Hasegawa, H. Akiyama, K. Ikeda, T. Nonaka, H. Mori, D. Mann, K. Tsuchiya, M. Yoshida, Y. Hashizume, T. Oda, TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 602–611 (2006). - PubMed
-
- M. Neumann, D. M. Sampathu, L. K. Kwong, A. C. Truax, M. C. Micsenyi, T. T. Chou, J. Bruce, T. Schuck, M. Grossman, C. M. Clark, L. F. McCluskey, B. L. Miller, E. Masliah, I. R. Mackenzie, H. Feldman, W. Feiden, H. A. Kretzschmar, J. Q. Trojanowski, V. M. Lee, Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314, 130–133 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

