Erdafitinib in patients with advanced solid tumours with FGFR alterations (RAGNAR): an international, single-arm, phase 2 study
- PMID: 37541273
- PMCID: PMC11224843
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00275-9
Erdafitinib in patients with advanced solid tumours with FGFR alterations (RAGNAR): an international, single-arm, phase 2 study
Abstract
Background: FGFR alterations are reported across various malignancies and might act as oncogenic drivers in multiple histologies. Erdafitinib is an oral, selective pan-FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor with activity in FGFR-altered advanced urothelial carcinoma. We aimed to evaluate the safety and activity of erdafitinib in previously treated patients with FGFR-altered advanced solid tumours.
Methods: The single-arm, phase 2 RAGNAR study was conducted at 156 investigative centres (hospitals or oncology practices that are qualified oncology study centres) across 15 countries. The study consisted of four cohorts based on tumour histology and patient age; the results reported in this Article are for the primary cohort of the study, defined as the Broad Panel Cohort, which was histology-agnostic. We recruited patients aged 12 years or older with advanced or metastatic tumours of any histology (except urothelial cancer) with predefined FGFR1-4 alterations (mutations or fusions according to local or central testing). Eligible patients had disease progression on at least one previous line of systemic therapy and no alternative standard therapy available to them, and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-1 (or equivalent for adolescents aged 12-17 years). Patients received once-daily oral erdafitinib (8 mg/day with provision for pharmacodynamically guided up-titration to 9 mg/day) on a continuous 21-day cycle until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. The primary endpoint was objective response rate by independent review committee according to Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST), version 1.1, or Response Assessment In Neuro-Oncology (RANO). The primary analysis was conducted on the treated population of the Broad Panel Cohort. This ongoing study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT04083976.
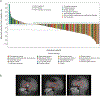
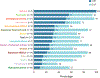
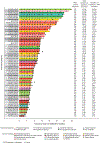
Findings: Patients were recruited between Dec 5, 2019, and Feb 15, 2022. Of 217 patients treated with erdafitinib, 97 (45%) patients were female and 120 (55%) were male. The data cutoff was Aug 15, 2022. At a median follow-up of 17·9 months (IQR 13·6-23·9), an objective response was observed in 64 (30% [95% CI 24-36]) of 217 patients across 16 distinct tumour types. The most common grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events related to erdafitinib were stomatitis (25 [12%]), palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia syndrome (12 [6%]), and hyperphosphataemia (11 [5%]). The most commonly occurring serious treatment-related adverse events (grade 3 or higher) were stomatitis in four (2%) patients and diarrhoea in two (1%). There were no treatment-related deaths.
Interpretation: RAGNAR results show clinical benefit for erdafitinib in the tumour-agnostic setting in patients with advanced solid tumours with susceptible FGFR alterations who have exhausted other treatment options. These results support the continued development of FGFR inhibitors in patients with advanced solid tumours.
Funding: Janssen Research & Development.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests SP has received consulting fees from Ipsen, Janssen, Novartis, and Zymeworks; and institutional research funding from 4D Pharma, Arcus Biosciences, Astellas Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Elicio Therapeutics, Janssen, Lilly, Mirati Therapeutics, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Purple Biotech, Rgenix, and Xencor. MS has received consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen Oncology, Merck Serono, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; honoraria from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen-Cilag, and Novartis; institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Bristol Myers Squibb; and has institutional patents, royalties, or other intellectual property for a highly sensitive method for mutation detection by PCR. GI has received consulting fees from Basilea, Bayer, Flare Therapeutics, Janssen, Loxo/Lilly, and Mirati Therapeutics; speakers’ bureau fees from Gilead Sciences and Lynx Group; and institutional research funding from Bayer, Debiopharm Group, Janssen, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis, and Seagen. OW has received consulting fees from Bayer US, LCC, Bristol Myers Squibb, Day One Therapeutics, Novartis, and Roche; and research funding from AstraZeneca, Bayer US, LLC, Blueprint Medicines, Day One Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Lilly, Loxo, Novartis, and Roche. TD has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen, Kaken Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Kirin, MSD, Otsuka, PRA Health Science, Rakuten Medical, Shionogi, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, and Takeda; honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb Japan, Chugai Pharma, Daicchi Sankyo, Ono Pharmaceutical, Rakuten Medical Japan, and Taiho Pharmaceutical; and institutional research funding from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, IQVIA, Janssen, MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical, Novartis, Pfizer, PRA Health Sciences, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, and Taiho Pharmaceutical. JT has received consulting fees from Array BioPharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardiff Oncology, Chugai Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, F Hoffman LaRoche, Genentech, HalioDx, Ikena Oncology, Inspirna, IQVIA, Lilly, Menarini, Merck Serono, Merus, Mirati Therapeutics, MSD, NeoPhore, Ona Therapeutics, Orion Biotechnology, Hutchison MediPharma, Novartis, Peptomyc, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, Scandion Oncology, Scorpion Therapeutics, Servier, Sotio, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Tessa Therapeutics, TheraMyc, and Tolremo; other financial interests from Imedex/HMP, Medscape, MJH Life Sciences, Peerview, Physicians’ Education Resource; and stock and other ownership interests from Oniria Therapeutics. DAR has received consulting fees from Advantagene, Agenus, Agios, AnHeart Therapeutics, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Delmar Pharmaceuticals, Ellipses Pharma, EMD Serono, Genenta Science, Imvax, Kintara Therapeutics, Kiyatec, Medicenna, Merck, Merck KGaA, Novocure, Oncorus, Regeneron, Taiho Pharmaceutical, and Vivacitas Oncology; honoraria from Advantagene, Agenus, AnHeart Therapeutics, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Deciphera, DelMar Pharmaceuticals, Ellipses Pharma, EMD Serono, Genenta Science, Imvax, Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Kintara Therapeutics, Kiyatec, Medicenna, Merck, Merck KGaA, Neuvogen, Oncorus, Novocure, Regeneron, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Vivacitas Oncology, and Y-mAbs Therapeutics; and institutional research funding from Acerta Pharma, Agenus, Celldex, EMD Serono, Enterome, Incyte, and Omniox. CM has received consulting fees from Amgen, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeiGene, Blueprint Medicines, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Debiopharm Group, Faron Pharmaceuticals, Genentech/Roche, Innate Pharma, Ipsen, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Orion, Pfizer, PharmaMar, Sanofi, and Taiho Pharmaceutical. AM has received consulting fees from Bayer, Chugai, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, and Novartis Oncology; has been reimbursed for travel, accommodations, or expenses from Amgen; and has received fees for participating in a data safety monitoring board or advisory board from Faron, Genmab, Janssen, Merck, and Takeda. IL has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim; honoraria from Agenus, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celon, Cullinan Oncology, Jacobio, Janssen, Loxo, Macrogenics, Menarini, MSD, Pfizer, Rhizen, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; institutional research funding from Agenus and Roche; and has been reimbursed for travel, accommodations, or expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb. OC has received consulting fees from Bayer US, LLC, and Janssen; honoraria from Bayer US, LLC, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer; and speakers’ bureau fees from Merck and Pfizer. DA has received consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Bristol Myers Squibb, CRA International, Gilead, Janssen Cilag, MSD, Onkowissen, Pierre Fabre Pharma, Seagen, and Terumo; honoraria from Amgen, Aptitude Health, Art Tempi Media, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, Bristol Myers Squibb, Clinical Care Options, Eisai, From Research to Practice, GlaxoSmithKline, Imedex, Ipsen, MCI, MedAhead (Austria), Merck Serono, MSD, Pierre Fabre Pharma, PRMA Consulting, Roche, Sanofi (Genzyme), Seagen, Servier, Streamitup Germany, Tactics MD LLC, Terumo, Viatris, and WebMD; fees for editorial roles with Elsevier; fees and an institutional education grant from AbbVie; institutional trial support from Bristol Myers Squibb and Oncolytics; and has served in a leadership role with EORTC. MG has received consulting fees from Celularity and Guardant. HW has received honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis; and has been reimbursed for travel, accommodations, or expenses from Janssen. KS, LC, SN, CH, STh, AS-W, STr, and HS received personal fees from Janssen during the conduct of the study. YL has received consulting fees from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Immunomedics, Janssen (personal and institutional), MSD Oncology (personal and institutional), Loxo/Lilly, Pfizer/EMD Serono, Roche, and Taiho Pharmaceutical; has been reimbursed for travel, accommodations, or expenses from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Janssen Oncology, MSD Oncology, and Roche; and has received institutional research funding from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Basilea, Bristol Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Gilead Sciences, Incyte, Janssen Oncology, Merck KGaA, MSD Oncology, Nektar, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and Taiho Pharmaceutical. SQ declares no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Katoh M Fibroblast growth factor receptors as treatment targets in clinical oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2019; 16: 105–22. - PubMed
-
- US Food & Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pemigatinib for cholangiocarcinoma with an FGFR2 rearrangement or fusion. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grant... (accessed February 28, 2023).
-
- US Food & Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to futibatinib for cholangiocarcinoma. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grant... (accessed February 28, 2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

