Anti-inflammatory potency of novel ecto-5'-nucleotidase/CD73 inhibitors in astrocyte culture model of neuroinflammation
- PMID: 37541364
- PMCID: PMC10527948
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175943
Anti-inflammatory potency of novel ecto-5'-nucleotidase/CD73 inhibitors in astrocyte culture model of neuroinflammation
Abstract
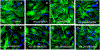
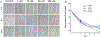
Three novel cytosine-derived α,β-methylene diphosphonates designated MRS4598, MRS4552, and MRS4602 were tested in the range of 1 × 10-9 to 1 × 10-3 M for their efficacy and potency in inhibiting membrane-bound ecto-5'-nucleotidase/CD73 activity in primary astrocytes in vitro. The compounds were also tested for their ability to attenuate the reactive astrocyte phenotype induced by proinflammatory cytokines. The main findings are as follows: A) The tested compounds induced concentration-dependent inhibition of CD73 activity, with maximal inhibition achieved at ∼1 × 10-3M; B) All compounds showed high inhibitory potency, as reflected by IC50 values in the submicromolar range; C) All compounds showed high binding capacity, as reflected by Ki values in the low nanomolar range; D) Among the tested compounds, MRS4598 showed the highest inhibitory efficacy and potency, as reflected by IC50 and Ki values of 0.11 μM and 18.2 nM; E) Neither compound affected astrocyte proliferation and cell metabolic activity at concentrations near to IC50; E) MRS4598 was able to inhibit CD73 activity in reactive astrocytes stimulated with TNF-α and to induce concentration-dependent inhibition of CD73 in reactive astrocytes stimulated with IL-1β, with an order of magnitude higher IC50 value; F) MRS4598 was the only compound tested that was able to induce shedding of the CD73 from astrocyte membranes and to enhance astrocyte migration in the scratch wound migration assay, albeit at concentration well above its IC50 value. Given the role of CD73 in neurodegenerative diseases, MRS4598, MRS4552, and MRS4602 are promising pharmacological tools for the treatment of neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Cell migration; Cytosine-based nucleoside 5'-α,β-methylene diphosphates; Ecto-5′-nucleotidase/CD73; Shedding.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors' individual contributions are listed in a separate section of the manuscript. The authors declare no professional, financial, personal, or other conflicts of interest. All authors have approved the manuscript and submission to European Journal of Pharmacology and agree with the order of authors in the manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Adzic M, Stevanovic I, Josipovic N, Laketa D, Lavrnja I, Bjelobaba IM, Bozic I, Jovanovic M, Milosevic M, Nedeljkovic N, 2017. Extracellular ATP induces graded reactive response of astrocytes and strengthens their antioxidative defense in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res 95,1053–1066. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23950. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

