Oxford brain health clinic: protocol and research database
- PMID: 37541753
- PMCID: PMC10407419
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-067808
Oxford brain health clinic: protocol and research database
Abstract
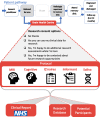
Introduction: Despite major advances in the field of neuroscience over the last three decades, the quality of assessments available to patients with memory problems in later life has barely changed. At the same time, a large proportion of dementia biomarker research is conducted in selected research samples that often poorly reflect the demographics of the population of patients who present to memory clinics. The Oxford Brain Health Clinic (BHC) is a newly developed clinical assessment service with embedded research in which all patients are offered high-quality clinical and research assessments, including MRI, as standard.
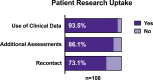
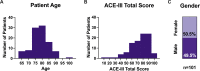
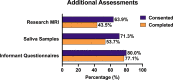
Methods and analysis: Here we describe the BHC protocol, including aligning our MRI scans with those collected in the UK Biobank. We evaluate rates of research consent for the first 108 patients (data collection ongoing) and the ability of typical psychiatry-led NHS memory-clinic patients to tolerate both clinical and research assessments.
Ethics and dissemination: Our ethics and consenting process enables patients to choose the level of research participation that suits them. This generates high rates of consent, enabling us to populate a research database with high-quality data that will be disseminated through a national platform (the Dementias Platform UK data portal).
Keywords: Dementia; Magnetic resonance imaging; Old age psychiatry; PSYCHIATRY.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CEM is a cofounder and shareholder of Exprodo Software, which was used to develop the BHC database. CEM serves on a Biogen Brain Health Consortium (unpaid). No other competing interests to report.
Figures
References
-
- Biogen . 221Ad302 phase 3 study of Aducanumab (Biib037) in early Alzheimer’s disease. 2015. Available: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02484547
-
- Biogen . 221Ad301 phase 3 study of Aducanumab (Biib037) in early Alzheimer’s disease. 2015. Available: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02477800
-
- Ngandu T, Lehtisalo J, Solomon A, et al. A 2 year Multidomain intervention of diet, exercise, cognitive training, and vascular risk monitoring versus control to prevent cognitive decline in at-risk elderly people (FINGER): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet 2015;385:2255–63. 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60461-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
