Rifampicin drug resistance and host immunity in tuberculosis: more than meets the eye
- PMID: 37543504
- PMCID: PMC11170062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2023.07.003
Rifampicin drug resistance and host immunity in tuberculosis: more than meets the eye
Abstract
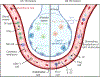
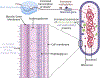
Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of death due to an infectious agent, with more than 1.5 million deaths attributed to TB annually worldwide. The global dissemination of drug resistance across Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) strains, causative of TB, resulted in an estimated 450 000 cases of drug-resistant (DR) TB in 2021. Dysregulated immune responses have been observed in patients with multidrug resistant (MDR) TB, but the effects of drug resistance acquisition and impact on host immunity remain obscure. In this review, we compile studies that span aspects of altered host-pathogen interactions and highlight research that explores how drug resistance and immunity might intersect. Understanding the immune processes differentially induced during DR TB would aid the development of rational therapeutics and vaccines for patients with MDR TB.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; altered immunity; drug-resistance; host–pathogen interactions; rifampicin.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests None declared by authors.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (2022) Global tuberculosis report 2022. Geneva. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Goldstein BP (2014) Resistance to rifampicin: a review. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 67, 625–630 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

