Structural basis for respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus neutralization
- PMID: 37544710
- PMCID: PMC10421620
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2023.101337
Structural basis for respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus neutralization
Abstract
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and human metapneumovirus (hMPV) continue to be a global burden to infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. In the past ten years, there has been substantial progress in the development of new vaccine candidates and therapies against these viruses. These advancements were guided by the structural elucidation of the major surface glycoproteins for these viruses, the fusion (F) protein and attachment (G) protein. The identification of immunodominant epitopes on the RSV F and hMPV F proteins has expanded current knowledge on antibody-mediated immune responses, which has led to new approaches for vaccine and therapeutic development through the stabilization of pre-fusion constructs of the F protein and pre-fusion-specific monoclonal antibodies with high potency and efficacy. In this review, we describe structural characteristics of known antigenic sites on the RSV and hMPV proteins, their influence on the immune response, and current progress in vaccine and therapeutic development.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest J.J.M. is listed as an inventor on patent applications related to RSV and hMPV monoclonal antibodies and vaccines.
Figures
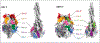
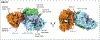
References
-
- Szabo SM, Gooch KL, Bibby MM, Vo PG, Mitchell I, Bradt P, et al. PaediatricRespiratory Reviews 13(S2) (2012) S1–S8 Paediatric Respiratory Reviews The risk of mortality among young children hospitalized for severe respiratory syncytial virus infection. 2012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

