Targeted degradation of MERTK and other TAM receptor paralogs by heterobifunctional targeted protein degraders
- PMID: 37545504
- PMCID: PMC10397400
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1135373
Targeted degradation of MERTK and other TAM receptor paralogs by heterobifunctional targeted protein degraders
Abstract
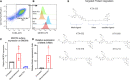
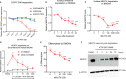
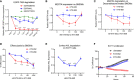
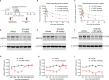
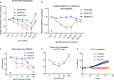
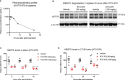
TAM receptors (TYRO3, AXL, and MERTK) comprise a family of homologous receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) that are expressed across a range of liquid and solid tumors where they contribute to both oncogenic signaling to promote tumor proliferation and survival, as well as expressed on myeloid and immune cells where they function to suppress host anti-tumor immunity. In recent years, several strategies have been employed to inhibit TAM kinases, most notably small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors and inhibitory neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that block receptor dimerization. Targeted protein degraders (TPD) use the ubiquitin proteasome pathway to redirect E3 ubiquitin ligase activity and target specific proteins for degradation. Here we employ first-in-class TPDs specific for MERTK/TAMs that consist of a cereblon E3 ligase binder linked to a tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting MERTK and/or AXL and TYRO3. A series of MERTK TPDs were designed and investigated for their capacity to selectively degrade MERTK chimeric receptors, reduce surface expression on primary efferocytic bone marrow-derived macrophages, and impact on functional reduction in efferocytosis (clearance of apoptotic cells). We demonstrate proof-of-concept and establish that TPDs can be tailored to either selectivity degrades MERTK or concurrently degrade multiple TAMs and modulate receptor expression in vitro and in vivo. This work demonstrates the utility of proteome editing, enabled by tool degraders developed here towards dissecting the therapeutically relevant pathway biology in preclinical models, and the ability for TPDs to degrade transmembrane proteins. These data also provide proof of concept that TPDs may serve as a viable therapeutic strategy for targeting MERTK and other TAMs and that this technology could be expanded to other therapeutically relevant transmembrane proteins.
Keywords: AXL; MERTK; TAM receptors; TYRO3; heterobifunctional targeted protein degraders; receptor down-regulation.
Copyright © 2023 Gadiyar, Patel, Chen, Vigil, Ji, Campbell, Sharma, Shi, Weiss, Birge and Davra.
Conflict of interest statement
VC, MW, KS and YS are currently employees and JC, DV and NJ are former employees at Kymera therapeutics. VD is employed by Xencor Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases Tyro3, Axl, and Mertk differentially contribute to antibody-induced arthritis.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Aug 3;21(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01133-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37537628 Free PMC article.
-
Axl and Mertk Receptors Cooperate to Promote Breast Cancer Progression by Combined Oncogenic Signaling and Evasion of Host Antitumor Immunity.Cancer Res. 2021 Feb 1;81(3):698-712. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2066. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33239426 Free PMC article.
-
Tyro3, Axl, and Mertk receptors differentially participate in platelet activation and thrombus formation.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Dec 12;16(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0308-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 30541554 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Tyro3, Axl and MerTK (TAM receptors): implications for macrophages in the tumor microenvironment.Mol Cancer. 2019 May 14;18(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1022-2. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31088471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TAM-ing T cells in the tumor microenvironment: implications for TAM receptor targeting.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020 Feb;69(2):237-244. doi: 10.1007/s00262-019-02421-w. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020. PMID: 31664482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring tumor-associated macrophages in glioblastoma: from diversity to therapy.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 May 2;9(1):126. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-00920-x. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40316746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Correlate with Disease Severity and Predict the Early Responsiveness of Sublingual Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Oct 25;16:4845-4855. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S432281. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37904786 Free PMC article.
-
MERTK Inhibition as a Targeted Novel Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 12;25(14):7660. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147660. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting tumor-associated macrophages with nanocarrier-based treatment for breast cancer: A step toward developing innovative anti-cancer therapeutics.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 30;10(18):e37217. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37217. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39309874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Tolerogenic Influence of Dexamethasone on Dendritic Cells Is Accompanied by the Induction of Efferocytosis, Promoted by MERTK.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 2;24(21):15903. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115903. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958886 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

