Disturbed lipid profile in common variable immunodeficiency - a pathogenic loop of inflammation and metabolic disturbances
- PMID: 37545531
- PMCID: PMC10398391
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1199727
Disturbed lipid profile in common variable immunodeficiency - a pathogenic loop of inflammation and metabolic disturbances
Abstract
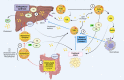
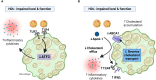
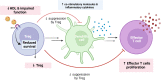
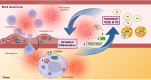
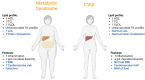
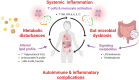
The relationship between metabolic and inflammatory pathways play a pathogenic role in various cardiometabolic disorders and is potentially also involved in the pathogenesis of other disorders such as cancer, autoimmunity and infectious diseases. Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is the most common primary immunodeficiency in adults, characterized by increased frequency of airway infections with capsulated bacteria. In addition, a large proportion of CVID patients have autoimmune and inflammatory complications associated with systemic inflammation. We summarize the evidence that support a role of a bidirectional pathogenic interaction between inflammation and metabolic disturbances in CVID. This include low levels and function of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), high levels of triglycerides (TG) and its major lipoprotein very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), and an unfavorable fatty acid (FA) profile. The dysregulation of TG, VLDL and FA were linked to disturbed gut microbiota profile, and TG and VLDL levels were strongly associated with lipopolysaccharides (LPS), a marker of gut leakage in blood. Of note, the disturbed lipid profile in CVID did not include total cholesterol levels or high low-density lipoprotein levels. Furthermore, increased VLDL and TG levels in blood were not associated with diet, high body mass index and liver steatosis, suggesting a different phenotype than in patients with traditional cardiovascular risk such as metabolic syndrome. We hypothesize that these metabolic disturbances are linked to inflammation in a bidirectional manner with disturbed gut microbiota as a potential contributing factor.
Keywords: CVID - common variable immunodeficiency; HDL - cholesterol; antibody deficiencies; fatty acids; inflammation; metabolism; triglycerid.
Copyright © 2023 Jorgensen, Macpherson, Skarpengland, Berge, Fevang, Halvorsen and Aukrust.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

