Co-Delivery Nanomicelles for Potentiating TNBC Immunotherapy by Synergetically Reshaping CAFs-Mediated Tumor Stroma and Reprogramming Immunosuppressive Microenvironment
- PMID: 37545872
- PMCID: PMC10403052
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S418100
Co-Delivery Nanomicelles for Potentiating TNBC Immunotherapy by Synergetically Reshaping CAFs-Mediated Tumor Stroma and Reprogramming Immunosuppressive Microenvironment
Abstract
Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have received the most attention for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), while the response rate to ICI remains limited due to insufficient T cell infiltration. It is therefore essential that alternative strategies are developed to improve the therapeutic outcomes of ICI in non-responsive TNBC cases. The efficacy of pH-responsive nanomicelles (P/A/B@NM) co-loaded with paclitaxel (PTX), CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100, and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor BMS-1 activating the T cell-mediated antitumor immune response were evaluated using a 4T1 antiPD-1-resistance breast tumor model.
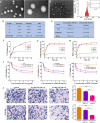
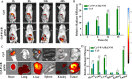
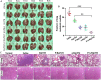
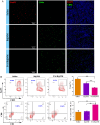
Methods: In vitro, pH-responsive antitumor effect of P/A/B@NM was investigated by assessing cell viability, migration and invasion. In vivo, the distribution of P/A/B@NM was visualized in 4T1 orthotopic TNBC model using an IVIS spectrum imaging instrument. The efficacy of the co-delivery nanocarriers was evaluated by monitoring mouse survival, tumor growth and metastasis, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs)-mediated tumor stroma and immunosuppressive microenvironment components, and the recruitment and infiltration of CD8+ T cells.
Results: The prepared P/A/B@NM in acid microenvironment demonstrates remarkable cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-231 cells, with an IC50 of 105 μg/mL. Additionally, it exhibits substantial inhibition of tumor cell migration and invasion. The P/A/B@NM based on co-delivery nanocarriers efficiently accumulate at the tumor site and release the drugs in a pH-responsive controlled manner. The nanomedicine-PTX, AMD3100, and BMS-1 formulation significantly inhibits tumor growth and lung/liver metastasis by inducing antitumor immune responses via CXCL12/CXCR4 axis blockade, and immunogenic cell death to reprogramme both tumor stroma and immunosuppressive microenvironment. As a result, CD8+ T cell infiltration is triggered into the tumor site, boosting the efficacy of ICI therapy synergistically.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that combination therapy using P/A/B@NM reshapes CAFs-mediated tumor stroma and immunosuppressive microenvironment, which can enhance the infiltration of CD8+ T cells, thereby reactivating anti-tumor immunity for non-responsive TNBC cases.
Keywords: CAFs; TNBC; co-delivery nanomicelles; immunosuppressive microenvironment; immunotherapy.
© 2023 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

