Pembrolizumab-Associated Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in a Patient With Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report
- PMID: 37546048
- PMCID: PMC10403812
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.41439
Pembrolizumab-Associated Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in a Patient With Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report
Abstract
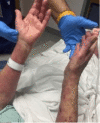
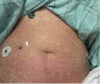
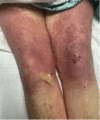
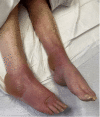
Pembrolizumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) receptor and is approved for the treatment of several malignancies. We present a rare case of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) occurring in a 75-year-old female 14 days after receiving the first dose of pembrolizumab therapy to treat stage IV non-small cell carcinoma of the lungs with metastasis to the brain. Although pruritus and papular, erythematous rashes are documented after its use, severe reactions such as SJS and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are rarely seen in clinical practice. In addition to supportive care, the patient also received intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and corticosteroid therapy and responded well to the therapy. Nearly complete re-epithelialization was achieved four weeks after the start of skin lesions. This case highlights a rare phenomenon of SJS- and TEN-associated adverse reactions following treatment with pembrolizumab.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; dermato-oncology; metastatic non-small cell lung cancer; pembrolizumab cutaneous side effect; stevens-johnson syndrome.
Copyright © 2023, Sandhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
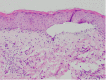
Figures
References
-
- Immunological response in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Abe R. J Dermatol. 2015;42:42–48. - PubMed
-
- Pembrolizumab-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient with metastatic cervical squamous cell carcinoma: a case report. Robinson S, Saleh J, Curry J, Mudaliar K. Am J Dermatopathol. 2020;42:292–296. - PubMed
-
- SCORTEN: a severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. Bastuji-Garin S, Fouchard N, Bertocchi M, Roujeau JC, Revuz J, Wolkenstein P. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:149–153. - PubMed
-
- Pembrolizumab induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. Kumar R, Bhandari S. Curr Probl Cancer. 2020;44:100478. - PubMed
-
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with pembrolizumab. Cai ZR, Lecours J, Adam JP, et al. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020;26:1259–1265. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
