A Mendelian randomization study for drug repurposing reveals bezafibrate and fenofibric acid as potential osteoporosis treatments
- PMID: 37547327
- PMCID: PMC10397407
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1211302
A Mendelian randomization study for drug repurposing reveals bezafibrate and fenofibric acid as potential osteoporosis treatments
Abstract
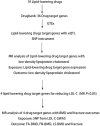
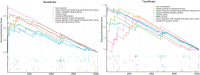
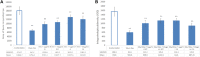
Background: Lipid pathways have been implicated in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis (OP). Lipid-lowering drugs may be used to prevent and treat OP. However, the causal interpretation of results from traditional observational designs is controversial by confounding. We aimed to investigate the causal association between genetically proxied lipid-lowering drugs and OP risk. Methods: We conducted two-step Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses to investigate the causal association of genetically proxied lipid-lowering drugs on the risk of OP. The first step MR was used to estimate the associations of drug target genes expression with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels. The significant SNPs in the first step MR were used as instrumental variables in the second step MR to estimate the associations of LDL-C levels with forearm bone mineral density (FA-BMD), femoral neck BMD (FN-BMD), lumbar spine BMD (LS-BMD) and fracture. The significant lipid-lowering drugs after MR analyses were further evaluated for their effects on bone mineralization using a dexamethasone-induced OP zebrafish model. Results: The first step MR analysis found that the higher expression of four genes (HMGCR, NPC1L1, PCSK9 and PPARG) was significantly associated with a lower LDL-C level. The genetically decreased LDL-C level mediated by the PPARG was significantly associated with increased FN-BMD (BETA = -1.38, p = 0.001) and LS-BMD (BETA = -2.07, p = 3.35 × 10-5) and was marginally significantly associated with FA-BMD (BETA = -2.36, p = 0.008) and reduced fracture risk (OR = 3.47, p = 0.008). Bezafibrate (BZF) and Fenofibric acid (FBA) act as PPARG agonists. Therefore genetically proxied BZF and FBA had significant protective effects on OP. The dexamethasone-induced OP zebrafish treated with BZF and FBA showed increased bone mineralization area and integrated optical density (IOD) with alizarin red staining. Conclusion: The present study provided evidence that BZF and FBA can increase BMD, suggesting their potential effects in preventing and treating OP. These findings potentially pave the way for future studies that may allow personalized selection of lipid-lowering drugs for those at risk of OP.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; bezafibrate and fenofibric acid; drug repurposing; lipid-lowering drugs; osteoporosis.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Pang, Zhang, Liu, Yi, Wang, Zhang, Deng, Chen, Greenbaum, Xiao, Deng and Tan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigating the causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and osteoporosis in the European population: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 8;14:1163258. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1163258. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37359532 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically determined type 1 diabetes mellitus and risk of osteoporosis.Exp Gerontol. 2024 Jun 15;191:112434. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112434. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Exp Gerontol. 2024. PMID: 38636571
-
Association between sarcopenia and osteoporosis: the cross-sectional study from NHANES 1999-2020 and a bi-directions Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 8;15:1399936. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1399936. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39439568 Free PMC article.
-
Positive effects of low LDL-C and statins on bone mineral density: an integrated epidemiological observation analysis and Mendelian randomization study.Int J Epidemiol. 2020 Aug 1;49(4):1221-1235. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyz145. Int J Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 31302685
-
The Effect of Plasma Lipids and Lipid-Lowering Interventions on Bone Mineral Density: A Mendelian Randomization Study.J Bone Miner Res. 2020 Jul;35(7):1224-1235. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3989. Epub 2020 Mar 12. J Bone Miner Res. 2020. PMID: 32163637
Cited by
-
Identification of Novel Protein Biomarkers and Drug Targets for Acne Vulgaris by Integrating Human Plasma Proteome with Genome-Wide Association Data.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 9;17:4431-4441. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S463450. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39006495 Free PMC article.
-
NPC1L1 Drives Osteoporosis by Activating the C/EBPα/Cyp27a1/27-Hydroxycholesterol Axis: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Bone Loss.FASEB Bioadv. 2025 May 8;7(6):e70020. doi: 10.1096/fba.2025-00044. eCollection 2025 Jun. FASEB Bioadv. 2025. PMID: 40496351 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

