Clopidogrel-Induced Eosinophilic Colitis
- PMID: 37547482
- PMCID: PMC10400044
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001118
Clopidogrel-Induced Eosinophilic Colitis
Abstract
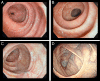
Eosinophilic colitis is a rare condition characterized by histologic findings of high eosinophilic infiltrate in the gut wall, typically presenting with diarrhea and abdominal pain. The etiology of this entity remains unclear because it can be primary or can occur secondarily to infections, drugs, or even in association with immune-mediated diseases. We present the case of a woman referred to our outpatient clinic for chronic diarrhea that had been worsening for months. Colonoscopy with biopsies was performed, and eosinophilic colitis associated with the use of clopidogrel was diagnosed. After clopidogrel discontinuation, a complete remission of the clinical and histological picture was observed.
Keywords: antiplatelet drugs; eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease; histology.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

