Mechanosensitive ion channels MSL8, MSL9, and MSL10 have environmentally sensitive intrinsically disordered regions with distinct biophysical characteristics in vitro
- PMID: 37547488
- PMCID: PMC10400277
- DOI: 10.1002/pld3.515
Mechanosensitive ion channels MSL8, MSL9, and MSL10 have environmentally sensitive intrinsically disordered regions with distinct biophysical characteristics in vitro
Abstract
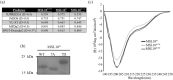
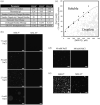
Intrinsically disordered protein regions (IDRs) are highly dynamic sequences that rapidly sample a collection of conformations over time. In the past several decades, IDRs have emerged as a major component of many proteomes, comprising ~30% of all eukaryotic protein sequences. Proteins with IDRs function in a wide range of biological pathways and are notably enriched in signaling cascades that respond to environmental stresses. Here, we identify and characterize intrinsic disorder in the soluble cytoplasmic N-terminal domains of MSL8, MSL9, and MSL10, three members of the MscS-like (MSL) family of mechanosensitive ion channels. In plants, MSL channels are proposed to mediate cell and organelle osmotic homeostasis. Bioinformatic tools unanimously predicted that the cytosolic N-termini of MSL channels are intrinsically disordered. We examined the N-terminus of MSL10 (MSL10N) as an exemplar of these IDRs and circular dichroism spectroscopy confirms its disorder. MSL10N adopted a predominately helical structure when exposed to the helix-inducing compound trifluoroethanol (TFE). Furthermore, in the presence of molecular crowding agents, MSL10N underwent structural changes and exhibited alterations to its homotypic interaction favorability. Lastly, interrogations of collective behavior via in vitro imaging of condensates indicated that MSL8N, MSL9N, and MSL10N have sharply differing propensities for self-assembly into condensates, both inherently and in response to salt, temperature, and molecular crowding. Taken together, these data establish the N-termini of MSL channels as intrinsically disordered regions with distinct biophysical properties and the potential to respond uniquely to changes in their physiochemical environment.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; circular dichroism; intrinsically disordered protein; ion channel; mechanobiology; phase separation; transmembrane protein.
© 2023 The Authors. Plant Direct published by American Society of Plant Biologists and the Society for Experimental Biology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors did not report any conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nonpolar residues in the presumptive pore-lining helix of mechanosensitive channel MSL10 influence channel behavior and establish a nonconducting function.Plant Direct. 2018 Jun;2(6):e00059. doi: 10.1002/pld3.59. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Plant Direct. 2018. PMID: 30506019 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis MSL10 has a regulated cell death signaling activity that is separable from its mechanosensitive ion channel activity.Plant Cell. 2014 Jul;26(7):3115-31. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.128082. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25052715 Free PMC article.
-
Two MscS homologs provide mechanosensitive channel activities in the Arabidopsis root.Curr Biol. 2008 May 20;18(10):730-734. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.04.039. Curr Biol. 2008. PMID: 18485707
-
Functional unfoldomics: Roles of intrinsic disorder in protein (multi)functionality.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2024;138:179-210. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2023.11.001. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38220424 Review.
-
Intrinsically disordered protein regions and phase separation: sequence determinants of assembly or lack thereof.Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020 Dec 11;4(3):307-329. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20190164. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 33078839 Review.
Cited by
-
A mechanosensitive ion channel controls touch-triggered stigma movement through manipulation of calcium signature in Torenia.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 8;16(1):6296. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61770-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40628738 Free PMC article.
-
Open structure and gating of the Arabidopsis mechanosensitive ion channel MSL10.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 7;14(1):6284. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42117-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37805510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artur, M. A. S. , Rienstra, J. , Dennis, T. J. , Farrant, J. M. , Ligterink, W. , & Hilhorst, H. (2019). Structural plasticity of intrinsically disordered LEA proteins from Xerophyta schlechteri provides protection in vitro and in vivo . Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 1272. 10.3389/fpls.2019.01272 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

