A Population-Based Study of Unfavorable Prognostic Factors Associated With Pyogenic Liver Abscess
- PMID: 37547858
- PMCID: PMC10400158
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofad352
A Population-Based Study of Unfavorable Prognostic Factors Associated With Pyogenic Liver Abscess
Abstract
Background: Pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) is a rare entity that is associated with substantial mortality and morbidity. Our objective was to investigate variables associated with mortality and subsequent PLA in patients diagnosed with PLA in southern Sweden.
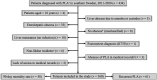
Methods: We conducted a population-based observational study comprising all episodes of PLA that occurred between 2011 and 2020 in the county of Skåne, southern Sweden. The primary outcome was defined as all-cause 90-day mortality and the secondary outcome was defined as the occurrence of a subsequent PLA.
Results: A total of 452 episodes of PLA occurred in 360 patients during the study period. The 90-day mortality rate was 16% (n = 58) and the subsequent PLA rate was 20% (n = 92). In a multivariable logistic regression model, female sex (odds ratio [OR], 2.0 [95% confidence interval {CI}, 1.1-3.9]), malignancy (OR, 3.7 [95% CI, 1.9-7.1]), liver failure (OR, 6.3 [95% CI, 2.7-14.5]), and polymicrobial findings (OR, 3.8 [95% CI, 2.2-6.9]) were associated with death within 90 days (P < .05). Male sex (OR, 2.1 [95% CI, 1.2-3.6]), malignancy (OR, 2.1 [95% CI, 1.3-3.6]), age (64-74 years: OR, 2.5 [95% CI, 1.3-4.8]), and chronic liver disease (OR, 3.0 [95% CI, 1.4-6.5]) were associated with the risk of subsequent PLA (P ≤ .01).
Conclusions: Identifying different clinical variables associated with an unfavorable outcome may improve the management and treatment of patients with PLA and thus prevent the risk of death and subsequent PLA.
Keywords: bacterial infection; liver abscess; outcome; prognosis; risk factors.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Hansen PS, Schønheyder HC. Pyogenic hepatic abscess. A 10-year population-based retrospective study. APMIS 1998; 106:396–402. - PubMed
-
- Jepsen P, Vilstrup H, Schønheyder HC, Sørensen HT. A nationwide study of the incidence and 30-day mortality rate of pyogenic liver abscess in Denmark, 1977–2002. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 21:1185–8. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan GG, Gregson DB, Laupland KB. Population-based study of the epidemiology of and the risk factors for pyogenic liver abscess. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 2:1032–8. - PubMed
-
- Meddings L, Myers RP, Hubbard J, et al. A population-based study of pyogenic liver abscesses in the United States: incidence, mortality, and temporal trends. Am J Gastroenterol 2010; 105:117–24. - PubMed

