Motor rehabilitation after stroke: European Stroke Organisation (ESO) consensus-based definition and guiding framework
- PMID: 37548025
- PMCID: PMC10683740
- DOI: 10.1177/23969873231191304
Motor rehabilitation after stroke: European Stroke Organisation (ESO) consensus-based definition and guiding framework
Abstract
Purpose: To propose a consensus-based definition and framework for motor rehabilitation after stroke.
Methods: An expert European working group reviewed the literature, attaining internal consensus after external feedback.
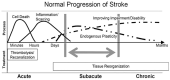
Findings: Motor rehabilitation is defined as a process that engages people with stroke to benefit their motor function, activity capacity and performance in daily life. It is necessary for people with residual motor disability whose goal is to enhance their functioning, independence and participation. Motor rehabilitation operates through learning- and use-dependent mechanisms. The trajectory of motor recovery varies across patients and stages of recovery. Early behavioral restitution of motor function depends on spontaneous biological mechanisms. Further improvements in activities of daily living are achieved by compensations. Motor rehabilitation is guided by regular assessment of motor function and activity using consensus-based measures, including patient-reported outcomes. Results are discussed with the patient and their carers to set personal goals. During motor rehabilitation patients learn to optimize and adapt their motor, sensory and cognitive functioning through appropriately dosed repetitive, goal-oriented, progressive, task- and context-specific training. Motor rehabilitation supports people with stroke to maximize health, well-being and quality of life. The framework describes the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health in the context of stroke, describes neurobiological mechanisms of behavioral restitution and compensation, and summarizes recommendations for clinical assessment, prediction tools, and motor interventions with strong recommendations from clinical practice guidelines (2016-2022).
Conclusions: This definition and framework may guide clinical educators, inform clinicians on current recommendations and guidelines, and identify gaps in the evidence base.
Keywords: Review; assessment; intervention; motor recovery; motor rehabilitation; prediction.
© European Stroke Organisation 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Feigin VL, Brainin M, Norrving B, et al. World Stroke Organization (WSO): global stroke fact sheet 2022. Int J Stroke 2022; 17: 18–29. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), World Bank. World report on disability. Geneva: WHO, 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

