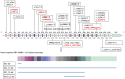
Mutation spectrum of retinoblastoma patients in Vietnam
- PMID: 37548407
- PMCID: PMC10655509
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.2244
Mutation spectrum of retinoblastoma patients in Vietnam
Abstract
Background: Retinoblastoma (RB), an intraocular malignancy commonly diagnosed in children, is mostly caused by inactivating mutations of both alleles of the RB1 gene. Early genetic screening for RB1 gene mutations would greatly improve treatment outcomes and patient management.
Methods: In this study, both somatic and germline mutations were detected in blood and tumour samples of 42 RB patients using direct sequencing and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification.
Results: In total, 34 different mutations were found in 36 patients, including 1 SNP, 4 large deletions, 5 splicing sites, 1 missense, 7 frameshifts and 17 nonsense mutations. There were five novel mutations and one unreported which have not been found in large databases such as Leiden Open Variation Database (LOVD) and ClinVar.
Conclusion: A higher rate of RB patients carrying heterozygous germline mutation and highly prevalent with pathogenic truncated mutation, hence, early detection of RB is essential for vision salvation and genetic counselling.
Keywords: MLPA; RB1 gene; mutation; retinoblastoma; sequencing.
© 2023 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abouzeid, H. , Munier, F. L. , Thonney, F. , & Schorderet, D. F. (2007). Ten novel RB1 gene mutations in patients with retinoblastoma. Molecular Vision, 13, 1740–1745. http://www.molvis.org/molvis/v13/a194 - PubMed
-
- Blixt, M. K. E. , Hellsand, M. , Konjusha, D. , Zhang, H. , Stenfelt, S. , Åkesson, M. , Rafati, N. , Tararuk, T. , Stålhammar, G. , All‐Eriksson, C. , Ring, H. , & Hallböök, F. (2022). MYCN induces cell‐specific tumorigenic growth in RB1‐proficient human retinal organoid and chicken retina models of retinoblastoma. Oncogenesis, 11(1), 1–13. 10.1038/s41389-022-00409-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous