The ReadFree tool for the identification of poor readers: a validation study based on a machine learning approach in monolingual and minority-language children
- PMID: 37548832
- PMCID: PMC10522748
- DOI: 10.1007/s11881-023-00287-3
The ReadFree tool for the identification of poor readers: a validation study based on a machine learning approach in monolingual and minority-language children
Abstract
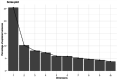
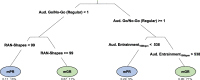
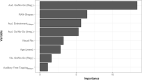
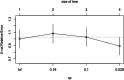
In this study, we validated the "ReadFree tool", a computerised battery of 12 visual and auditory tasks developed to identify poor readers also in minority-language children (MLC). We tested the task-specific discriminant power on 142 Italian-monolingual participants (8-13 years old) divided into monolingual poor readers (N = 37) and good readers (N = 105) according to standardised Italian reading tests. The performances at the discriminant tasks of the "ReadFree tool" were entered into a classification and regression tree (CART) model to identify monolingual poor and good readers. The set of classification rules extracted from the CART model were applied to the MLC's performance and the ensuing classification was compared to the one based on standardised Italian reading tests. According to the CART model, auditory go-no/go (regular), RAN and Entrainment100bpm were the most discriminant tasks. When compared with the clinical classification, the CART model accuracy was 86% for the monolinguals and 76% for the MLC. Executive functions and timing skills turned out to have a relevant role in reading. Results of the CART model on MLC support the idea that ad hoc standardised tasks that go beyond reading are needed.
Keywords: Bilingualism; Classification and regression tree (CART) model; Developmental dyslexia; Executive functions; Timing skills.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Anastasi A. Evolving concepts of test validation. Annual Review of Psychology. 1986;37(1):1–16. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.37.020186.000245. - DOI
-
- American Psychiatric Association, D. S. M. T. F., & American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5 (Vol. 5, No. 5). Washington, DC: American psychiatric association.
-
- Araújo S, Faísca L. A meta-analytic review of naming-speed deficits in developmental dyslexia. Scientific Studies of Reading. 2019;23(5):349–368. doi: 10.1080/10888438.2019.1572758. - DOI
-
- Arikan S, van de Vijver FJ, Yagmur K. PISA mathematics and reading performance differences of mainstream European and Turkish immigrant students. Educational Assessment, Evaluation and Accountability. 2017;29(3):229–246. doi: 10.1007/s11092-017-9260-6. - DOI
-
- Asri H, Mousannif H, Al Moatassime H, Noel T. Using machine learning algorithms for breast cancer risk prediction and diagnosis. Procedia Computer Science. 2016;83:1064–1069. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.04.224. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

