Metabolic implications and safety of dolutegravir use in pregnancy
- PMID: 37549681
- PMCID: PMC11100098
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-3018(23)00141-8
Metabolic implications and safety of dolutegravir use in pregnancy
Abstract
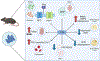
Dolutegravir is recommended for all people living with HIV because of its efficacy, high barrier to resistance, favourable safety and tolerability profile, and affordability. Dolutegravir has the highest rates of viral suppression in pregnancy, therefore preventing perinatal HIV transmission. In view of these benefits, particularly for pregnant women, an important question is if dolutegravir is safe in pregnancy. Dolutegravir has been associated with metabolic complications, including weight gain and rare events of hyperglycaemia, that could affect maternal, fetal, and postnatal health. We review the current clinically and experimentally based literature on the implications of dolutegravir use for pregnant women and for developing embryos and fetuses. Possible effects on folate status, energy metabolism, adipogenesis, and oxidative stress are considered. In many instances, insufficient data are available, pointing to the need for additional research in this important area of HIV treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pandey A, Galvani AP. The global burden of HIV and prospects for control. Lancet HIV. 2019; 6: e809–11. - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS. Understanding Fast-Track Targets. Accelerating action to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030. UNAIDS; 2015.
-
- Panel on Treatment of HIV During Pregnancy and Prevention of Perinatal Transmission. Recommendations for the Use of Antiretroviral Drugs During Pregnancy and Interventions to Reduce Perinatal HIV Transmission in the United States [Internet]. Department of Health and Human Services; Available from: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/guidelines/perinatal.
-
- Sibiude J, Le Chenadec J, Mandelbrot L, Hoctin A, Dollfus C, Faye A, et al. Update of Perinatal Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Transmission in France: Zero Transmission for 5482 Mothers on Continuous Antiretroviral Therapy From Conception and With Undetectable Viral Load at Delivery. Clin Infect Dis. 2023; 76: e590–8. - PubMed
-
- Consolidated guidelines on HIV prevention, testing, treatment, service delivery and monitoring: recommendations for a public health approach. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

