Prevalence of Soil-Transmitted Helminths at Baseline and after Albendazole Treatment in the School-Age Children of Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals in Bangladesh
- PMID: 37549897
- PMCID: PMC10484276
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.23-0260
Prevalence of Soil-Transmitted Helminths at Baseline and after Albendazole Treatment in the School-Age Children of Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals in Bangladesh
Abstract
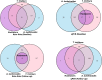
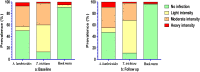
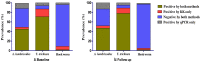
The forcibly displaced Myanmar nationals (FDMNs) known as Rohingya refugees are the largest group of stateless individuals globally. According to the emergencies humanitarian actors at the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, the worldwide refugee crisis involving FDMNs is intensifying at the fastest rate in history. Growing public health demands are being exacerbated by current difficulties in addressing poor access to health services, severe food shortages, and a lack of adequate housing. Infectious diseases constitute a major public health emergency in this vulnerable population. A study was carried out in FDMN children to investigate common soil-transmitted helminth (STH) infection at the time of enrollment and prospectively followed-up to 12 months after 2 doses albendazole treatment. At baseline, the prevalence of STH infection with at least one species was found to be 91.7% and 87.3% for Kato-Katz (KK) and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) methods, respectively. Similarly, for follow-up children, the overall infection rate was 95.3% and 91.5%, respectively. Trichuris trichiura was the most predominant STH infection by both KK (baseline 87%, follow-up 89.1%) and qPCR (baseline 77.5%, follow-up 82.9%). The overall prevalence of stunting in the children was 37.8% at baseline and rose to 51.3% at 12 months. Alpha-1 antitrypsin (r = 0.13, P = 0.01) and myeloperoxidase (r = 0.12, P = 0.01) levels showed a positive correlation with Aascaris lumbricoides egg count per gram at baseline. An in-depth investigation is urgently needed to identify the underlying protective measures and the root cause of STH infections to improve the health of FDMN children.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Performance of the Kato-Katz method and real time polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of soil-transmitted helminthiasis in the framework of a randomised controlled trial: treatment efficacy and day-to-day variation.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Oct 15;13(1):517. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04401-x. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 33059756 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of three copromicroscopic methods to assess albendazole efficacy against soil-transmitted helminth infections in school-aged children on Pemba Island.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2013 Aug;107(8):493-501. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trt051. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2013. PMID: 23843559 Clinical Trial.
-
A cross-sectional survey of soil-transmitted helminthiases in two Myanmar villages receiving mass drug administration: epidemiology of infection with a focus on adults.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Aug 4;10(1):374. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2306-2. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28778217 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine citrate, and albendazole mass drug administration on the prevalence of scabies and soil-transmitted helminths in school-aged children in three municipalities in Timor-Leste: a before-after assessment.Lancet Glob Health. 2023 Jun;11(6):e924-e932. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(23)00134-1. Lancet Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 37202027
-
A strong effect of individual compliance with mass drug administration for lymphatic filariasis on sustained clearance of soil-transmitted helminth infections.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Jun 8;14(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04814-2. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34103096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO , 2017. Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections: Fact Sheet. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization Media Centre.
-
- Hotez PJ, 2009. Mass drug administration and integrated control for the world’s high-prevalence neglected tropical diseases. Clin Pharmacol Ther 85: 659–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

