Generating fast-twitch myotubes in vitro with an optogenetic-based, quantitative contractility assay
- PMID: 37550008
- PMCID: PMC10427763
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202302227
Generating fast-twitch myotubes in vitro with an optogenetic-based, quantitative contractility assay
Abstract
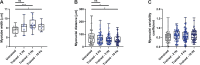
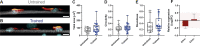
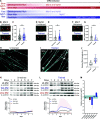
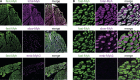
The composition of fiber types within skeletal muscle impacts the tissue's physiological characteristics and susceptibility to disease and ageing. In vitro systems should therefore account for fiber-type composition when modelling muscle conditions. To induce fiber specification in vitro, we designed a quantitative contractility assay based on optogenetics and particle image velocimetry. We submitted cultured myotubes to long-term intermittent light-stimulation patterns and characterized their structural and functional adaptations. After several days of in vitro exercise, myotubes contract faster and are more resistant to fatigue. The enhanced contractile functionality was accompanied by advanced maturation such as increased width and up-regulation of neuron receptor genes. We observed an up-regulation in the expression of fast myosin heavy-chain isoforms, which induced a shift towards a fast-twitch phenotype. This long-term in vitro exercise strategy can be used to study fiber specification and refine muscle disease modelling.
© 2023 Hennig et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
