STENCIL-NET for equation-free forecasting from data
- PMID: 37550328
- PMCID: PMC10406911
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-39418-6
STENCIL-NET for equation-free forecasting from data
Abstract
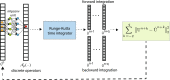
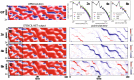
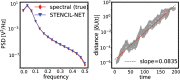
We present an artificial neural network architecture, termed STENCIL-NET, for equation-free forecasting of spatiotemporal dynamics from data. STENCIL-NET works by learning a discrete propagator that is able to reproduce the spatiotemporal dynamics of the training data. This data-driven propagator can then be used to forecast or extrapolate dynamics without needing to know a governing equation. STENCIL-NET does not learn a governing equation, nor an approximation to the data themselves. It instead learns a discrete propagator that reproduces the data. It therefore generalizes well to different dynamics and different grid resolutions. By analogy with classic numerical methods, we show that the discrete forecasting operators learned by STENCIL-NET are numerically stable and accurate for data represented on regular Cartesian grids. A once-trained STENCIL-NET model can be used for equation-free forecasting on larger spatial domains and for longer times than it was trained for, as an autonomous predictor of chaotic dynamics, as a coarse-graining method, and as a data-adaptive de-noising method, as we illustrate in numerical experiments. In all tests, STENCIL-NET generalizes better and is computationally more efficient, both in training and inference, than neural network architectures based on local (CNN) or global (FNO) nonlinear convolutions.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. This study contains no data obtained from human or living samples.
Figures







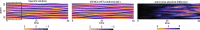


References
-
- Karnakov, P., Litvinov, S. & Koumoutsakos, P. Optimizing a DIscrete Loss (ODIL) to solve forward and inverse problems for partial differential equations using machine learning tools. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.04611 (2022).
-
- Pilva, P. & Zareei, A. Learning time-dependent PDE solver using message passing graph neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.07651 (2022).
Grants and funding
- EXC-2068/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- ScaDS.AI/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Federal Ministry of Education and Research)
- ScaDS.AI/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Federal Ministry of Education and Research)
- CASUS/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Federal Ministry of Education and Research)
- CASUS/Sächsisches Staatsministerium fü;r Wissenschaft und Kunst (Saxon State Ministry for Science and Art)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

