Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics define the natural history of autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37550416
- PMCID: PMC10427428
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-023-02476-4
Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics define the natural history of autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
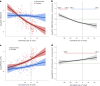
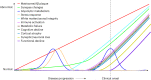
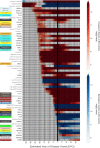
Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology develops many years before the onset of cognitive symptoms. Two pathological processes-aggregation of the amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide into plaques and the microtubule protein tau into neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs)-are hallmarks of the disease. However, other pathological brain processes are thought to be key disease mediators of Aβ plaque and NFT pathology. How these additional pathologies evolve over the course of the disease is currently unknown. Here we show that proteomic measurements in autosomal dominant AD cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) linked to brain protein coexpression can be used to characterize the evolution of AD pathology over a timescale spanning six decades. SMOC1 and SPON1 proteins associated with Aβ plaques were elevated in AD CSF nearly 30 years before the onset of symptoms, followed by changes in synaptic proteins, metabolic proteins, axonal proteins, inflammatory proteins and finally decreases in neurosecretory proteins. The proteome discriminated mutation carriers from noncarriers before symptom onset as well or better than Aβ and tau measures. Our results highlight the multifaceted landscape of AD pathophysiology and its temporal evolution. Such knowledge will be critical for developing precision therapeutic interventions and biomarkers for AD beyond those associated with Aβ and tau.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.M.D., N.T.S. and A.I.L. are founders of EmTheraPro. T.S.W. is a co-founder of revXon. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG072120/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG056533/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG061357/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UF1 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025214/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG075827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS092865/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG071170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG068604/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

