Exosomal-miR-129-2-3p derived from Fusobacterium nucleatum-infected intestinal epithelial cells promotes experimental colitis through regulating TIMELESS-mediated cellular senescence pathway
- PMID: 37550944
- PMCID: PMC10411316
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2240035
Exosomal-miR-129-2-3p derived from Fusobacterium nucleatum-infected intestinal epithelial cells promotes experimental colitis through regulating TIMELESS-mediated cellular senescence pathway
Abstract
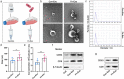
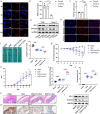
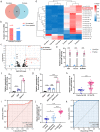
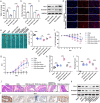
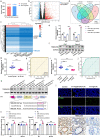
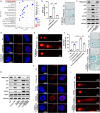
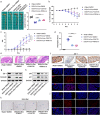
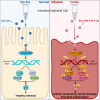
Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn) infection is known to exacerbate ulcerative colitis (UC). However, the link between Fn-infected intestinal epithelial cell (IEC)-derived exosomes (Fn-Exo) and UC progression has not been investigated. Differentially expressed miRNAs in Fn-Exo and non-infected IECs-derived exosomes (Con-Exo) were identified by miRNA sequencing. Then, the biological role and mechanism of Fn-Exo in UC development were determined in vitro and in vivo. We found that exosomes delivered miR-129-2-3p from Fn-infected IECs into non-infected IECs, exacerbating epithelial barrier dysfunction and experimental colitis. Mechanically, Fn-Exo induces DNA damage via the miR-129-2-3p/TIMELESS axis and subsequently activates the ATM/ATR/p53 pathway, ultimately promoting cellular senescence and colonic inflammation. In conclusion, Exo-miR-129-2-3p/TIMELESS/ATM/ATR/p53 pathway aggravates cellular senescence, barrier damage, and experimental colitis. The current study revealed a previously unknown regulatory pathway in the progression of Fn-infectious UC. Furthermore, Exosomal-miR-129-2-3p in serum and TIMELESS may function as novel potential diagnostic biomarkers for UC and Fn-high-UC.
Keywords: Fusobacterium nucleatum; TIMELESS; cellular senescence; exosomes; miR-129-2-3p; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
