Amlodipine in the current management of hypertension
- PMID: 37551050
- PMCID: PMC10497034
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.14709
Amlodipine in the current management of hypertension
Abstract
Hypertension is the leading cause of death worldwide, affecting 1.4 billion people. Treatment options include the widely used calcium channel blockers, among which amlodipine, a dihydropyridine, has unique characteristics that distinguish it from other drugs within this class. This review aims to provide an updated overview of the evidence supporting the use of amlodipine over the past 30 years and highlights its cardiovascular benefits in current hypertension management. Amlodipine has low renal clearance (7 mL/min/mg) and long half-life (35-50 h) and duration of action, which allows it to sustain its anti-hypertensive effect for more than 24 h following a single dose. Additionally, blood pressure (BP) control is maintained even when a dose has been missed, providing continuous protection in case of incidental noncompliance. It has proven to reduce BP variability and successfully lower BP. Amlodipine also controls BP in patients with a systolic/diastolic BP of 130/80 mm Hg or higher, diabetes, or chronic kidney disease without worsening glycemic or kidney function. Additionally, amlodipine is a wise choice for older adults due to its ability to control BP and protect against stroke and myocardial infarction. Side effects of amlodipine include edema, palpitations, dizziness, and flushing, which are more common with the higher dose of 10 mg. Amlodipine is cost effective and predicted to be cost saving when compared with usual care.
Keywords: amlodipine; blood pressure variability; calcium channel blockers; hypertension.
© 2023 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Jiguang Wang has received financial grants from Omron and has been paid as a speaker for Novartis, Omron, Servier, and Viatris. Peter Sever has received research grants from Pfizer, Servier, and Amgen; has worked as a paid consultant for Pfizer and Amgen; and has been a paid speaker for Pfizer, Amgen, and Viatris. All other authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
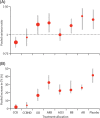
References
-
- Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A. International Society of Hypertension. Global burden of blood‐pressure‐related disease. Lancet. 2008;371(9623):1513‐1518. 2001. - PubMed
-
- Kario K, Tomitani N, Nishizawa M, Harada N, Kanegae H, Hoshide S. Concept, study design, and baseline blood pressure control status of the nationwide prospective HI‐JAMP study using multisensor ABPM. Hypertens Res. 2023;46(2):357‐367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

