Inhaled Volatile Molecules-Responsive TRP Channels as Non-Olfactory Receptors
- PMID: 37551139
- PMCID: PMC10902705
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2023.118
Inhaled Volatile Molecules-Responsive TRP Channels as Non-Olfactory Receptors
Abstract
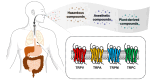
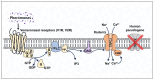
Generally, odorant molecules are detected by olfactory receptors, which are specialized chemoreceptors expressed in olfactory neurons. Besides odorant molecules, certain volatile molecules can be inhaled through the respiratory tract, often leading to pathophysiological changes in the body. These inhaled molecules mediate cellular signaling through the activation of the Ca2+-permeable transient receptor potential (TRP) channels in peripheral tissues. This review provides a comprehensive overview of TRP channels that are involved in the detection and response to volatile molecules, including hazardous substances, anesthetics, plant-derived compounds, and pheromones. The review aims to shed light on the biological mechanisms underlying the sensing of inhaled volatile molecules. Therefore, this review will contribute to a better understanding of the roles of TRP channels in the response to inhaled molecules, providing insights into their implications for human health and disease.
Keywords: Non-olfactory receptors; TRPA1; TRPV1; Transient receptor potential channel; Volatile organic compound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Andrè E., Campi B., Materazzi S., Trevisani M., Amadesi S., Massi D., Creminon C., Vaksman N., Nassini R., Civelli M., Baraldi P. G., Poole D. P., Bunnett N. W., Geppetti P., Patacchini R. Cigarette smoke-induced neurogenic inflammation is mediated by alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes and the TRPA1 receptor in rodents. J. Clin. Invest. 2008;118:2574–2582. doi: 10.1172/JCI34886. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

