Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomal miRNA-21-5p Inhibits Lidocaine-Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells
- PMID: 37551179
- PMCID: PMC10404314
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v52i4.12446
Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomal miRNA-21-5p Inhibits Lidocaine-Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells
Abstract
Background: Local anesthetic lidocaine is one of the most common pain therapies, but high concentration of lidocaine induced neurotoxicity and its mechanism is unclear. Exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) is implicated in neuronal diseases, but its role in lidocaine induced neurotoxicity remains to be elucidated.
Methods: All the experiments were performed at Huzhou Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, Huzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China in 2022. Lidocaine was used to induce apoptosis of SH-SY5Y cells. Exosomes isolated from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSC-exos) were used to co-treat SH-SY5Y cells with lidocaine. Cell apoptosis was measured using a flow cytometer. PKH-67 Dye was used for exosome uptake assay. miR-21-5p mimics/inhibitors, or negative controls were transfected with Lipo2000 to study its effect on lid-induced injury. Interactions between miR-21-5p and PDCD4 was analyzed by luciferase reporter assay.
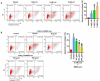
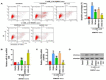
Results: Administration of BMSC-exo protected SH-SY5Y cells against lidocaine induced apoptosis. Suppressing miR-21-5p dramatically enhanced PDCD4, but miR-21-5p overexpression sharply down-regulated PDCD4. Mechanism study showed that miR-21-5p bound to 3'-UTR of PDCD4 to inhibit it. Suppressing miR-21-5p reversed the effect of BMSC-exo on Lid-induced injury. Results also indicate that miR-21-5p regulated lidocaine-induced injury through targeting PDCD4.
Conclusion: BMSC-exos protected SH-SY5Y cells against lidocaine induced apoptosis through miR-21-5p by targeting PDCD4, which may develop new strategy in the management of lidocaine-induced neurotoxicity.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Exosomes; Lidocaine; Microrna; Neuronal toxicity; Programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4).
Copyright © 2023 Chen et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exosomal microRNA-342-5p from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibits preeclampsia in rats.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Jan 4;23(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00931-y. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36598700
-
MicroRNA-183-5p protects human derived cell line SH-SY5Y cells from mepivacaine-induced injury.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3177-3187. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1946358. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34180760 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA LINC01347 Modulated Lidocaine-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells by Interacting with hsa-miR-145-5p.Neurotox Res. 2021 Oct;39(5):1440-1448. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00363-9. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Neurotox Res. 2021. PMID: 34115321
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate neuroinflammation after diabetic intracerebral hemorrhage via the miR-183-5p/PDCD4/NLRP3 pathway.J Endocrinol Invest. 2021 Dec;44(12):2685-2698. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01583-8. Epub 2021 May 23. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021. PMID: 34024028
-
Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-21-5p downregulates PDCD4 and ameliorates erectile dysfunction in a rat model of diabetes mellitus.FASEB J. 2020 Oct;34(10):13345-13360. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000102RR. Epub 2020 Aug 17. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32808325
References
-
- Wang B, Wang S, Zhang Q, et al. ( 2019). Recent advances in polymer-based drug delivery systems for local anesthetics. Acta Biomater, 96: 55–67. - PubMed
-
- Anderson T. ( 2016). Doctors lobby for better chronic pain management. Lancet, 388( 10062): 2856– 2858. - PubMed
-
- Kuehn B. ( 2018). Chronic Pain Prevalence. JAMA, 320( 16): 1632. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson M, Goodchild JH. ( 2018). Lidocaine turns 70: the evolution of dental local anesthesia. Gen Dent, 66( 3): 6–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
