The Effect of Human Development Index on Obesity Prevalence at the Global Level: A Spatial Analysis
- PMID: 37551189
- PMCID: PMC10404321
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v52i4.12456
The Effect of Human Development Index on Obesity Prevalence at the Global Level: A Spatial Analysis
Abstract
Background: Obesity is one of the major public health concerns, and its prevalence is increasing worldwide. This study aimed to investigate the effect of human development index on the prevalence of obesity across 152 countries.
Methods: Country-level data on obesity prevalence and its influencing variables related to 152 countries were obtained during 2000-2019 from several sources. A Spatial Bayesian Hierarchical model was employed in this research, and the analyses were performed using R statistical software (version 3.6.1).
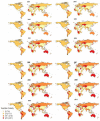
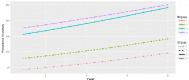
Results: We found a positive relation between HDI and obesity prevalence, in such a way if low HDI countries advance to high HDI countries, the obesity rate is expected to increase significantly by 7.45%. Moreover, the association between obesity prevalence and the percentage of people aged 40-59 (β=0.07), urbanization rate (β=0.11), percentage of internet users (β=0.01), percentage of alcohol users (β=0.16), milk consumption per capita (β=0.15) and Percentage of depression (β=0.58) was significantly positive. Conversely, per capita consumption of fruits and vegetables (β=-0.15), and smoking rate (β=-0.02) was negatively associated with obesity prevalence.
Conclusion: The prevalence of obesity is growing across all countries, especially in the countries with high and very high HDI. Therefore, policymakers must also pay attention to the negative effects of development when trying to improve the welfare of society.
Keywords: Human development index; Lifestyle factors; Obesity; Sociodemographic factors.
Copyright © 2023 Shirvani Shiri et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization ( 2018). Obesity and overweight. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
-
- Hosseinpanah F, Mirbolouk M, Mossadeghkhah A, et al. ( 2016). Incidence and potential risk factors of obesity among Tehranian adults. Prev Med, 82: 99–104. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
