EPAC1 inhibition protects the heart from doxorubicin-induced toxicity
- PMID: 37551870
- PMCID: PMC10484526
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.83831
EPAC1 inhibition protects the heart from doxorubicin-induced toxicity
Abstract
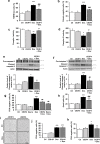
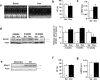
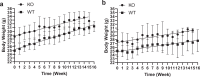
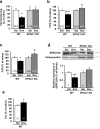
Anthracyclines, such as doxorubicin (Dox), are widely used chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. However, they frequently induce cardiotoxicity leading to dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. This study sought to investigate the role of the exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC) in Dox-induced cardiotoxicity and the potential cardioprotective effects of EPAC inhibition. We show that Dox induces DNA damage and cardiomyocyte cell death with apoptotic features. Dox also led to an increase in both cAMP concentration and EPAC1 activity. The pharmacological inhibition of EPAC1 (with CE3F4) but not EPAC2 alleviated the whole Dox-induced pattern of alterations. When administered in vivo, Dox-treated WT mice developed a dilated cardiomyopathy which was totally prevented in EPAC1 knock-out (KO) mice. Moreover, EPAC1 inhibition potentiated Dox-induced cell death in several human cancer cell lines. Thus, EPAC1 inhibition appears as a potential therapeutic strategy to limit Dox-induced cardiomyopathy without interfering with its antitumoral activity.
Keywords: EPAC1; cancer biology; cardiology; cardiotoxicity; cell biology; doxorubicin; human; mouse; rat.
© 2023, Mazevet et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MM, AB, MR, DD, AL, ML, TB, PM, MG, FL, JC, CB, CR, FL, BC, JB, MV, RF, AG, CL, EM No competing interests declared
Figures
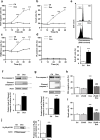
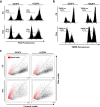
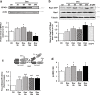
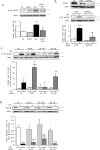
Comment in
-
Protecting the heart.Elife. 2023 Sep 6;12:e91831. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91831. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37672034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almahariq M, Chao C, Mei FC, Hellmich MR, Patrikeev I, Motamedi M, Cheng X. Pharmacological inhibition and genetic knockdown of exchange protein directly activated by cAMP 1 reduce pancreatic cancer metastasis in vivo. Molecular Pharmacology. 2015;87:142–149. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.095158. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baljinnyam E, Umemura M, Chuang C, De Lorenzo MS, Iwatsubo M, Chen S, Goydos JS, Ishikawa Y, Whitelock JM, Iwatsubo K. Epac1 increases migration of endothelial cells and melanoma cells via FGF2-mediated paracrine signaling. Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research. 2014;27:611–620. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12250. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown LM, Rogers KE, McCammon JA, Insel PA. Identification and validation of modulators of exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac) activity: structure-function implications for Epac activation and inhibition. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2014;289:8217–8230. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.548636. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

