Macrocephaly and developmental delay caused by missense variants in RAB5C
- PMID: 37552066
- PMCID: PMC10586195
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddad130
Macrocephaly and developmental delay caused by missense variants in RAB5C
Abstract
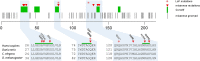
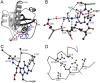
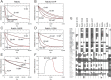
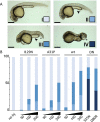
Rab GTPases are important regulators of intracellular vesicular trafficking. RAB5C is a member of the Rab GTPase family that plays an important role in the endocytic pathway, membrane protein recycling and signaling. Here we report on 12 individuals with nine different heterozygous de novo variants in RAB5C. All but one patient with missense variants (n = 9) exhibited macrocephaly, combined with mild-to-moderate developmental delay. Patients with loss of function variants (n = 2) had an apparently more severe clinical phenotype with refractory epilepsy and intellectual disability but a normal head circumference. Four missense variants were investigated experimentally. In vitro biochemical studies revealed that all four variants were damaging, resulting in increased nucleotide exchange rate, attenuated responsivity to guanine exchange factors and heterogeneous effects on interactions with effector proteins. Studies in C. elegans confirmed that all four variants were damaging in vivo and showed defects in endocytic pathway function. The variant heterozygotes displayed phenotypes that were not observed in null heterozygotes, with two shown to be through a dominant negative mechanism. Expression of the human RAB5C variants in zebrafish embryos resulted in defective development, further underscoring the damaging effects of the RAB5C variants. Our combined bioinformatic, in vitro and in vivo experimental studies and clinical data support the association of RAB5C missense variants with a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by macrocephaly and mild-to-moderate developmental delay through disruption of the endocytic pathway.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Zhen, Y. and Stenmark, H. (2015) Cellular functions of Rab GTPases at a glance. J. Cell Sci., 128, 3171–3176. - PubMed
-
- Lamers, I.J.C., Reijnders, M.R.F., Venselaar, H., Kraus, A., Study, D.D.D., Jansen, S., deVries, B.B.A., Houge, G., Gradek, G.A., Seo, J.et al. (2017) Recurrent De novo mutations disturbing the GTP/GDP binding pocket of RAB11B cause intellectual disability and a distinctive brain phenotype. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 101, 824–832. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giannandrea, M., Bianchi, V., Mignogna, M.L., Sirri, A., Carrabino, S., D’Elia, E., Vecellio, M., Russo, S., Cogliati, F., Larizza, L.et al. (2010) Mutations in the small GTPase gene RAB39B are responsible for X-linked mental retardation associated with autism, epilepsy, and macrocephaly. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 86, 185–195. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Veleri, S., Punnakkal, P., Dunbar, G.L. and Maiti, P. (2018) Molecular insights into the roles of Rab proteins in intracellular dynamics and neurodegenerative diseases. NeuroMolecular Med., 20, 18–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

