A phase I COVID-19 vaccine trial among SARS-CoV-2 seronegative and seropositive individuals in Uganda utilizing a self-amplifying RNA vaccine platform: Screening and enrollment experiences
- PMID: 37553178
- PMCID: PMC10411305
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2240690
A phase I COVID-19 vaccine trial among SARS-CoV-2 seronegative and seropositive individuals in Uganda utilizing a self-amplifying RNA vaccine platform: Screening and enrollment experiences
Abstract
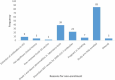
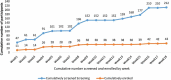
We report the screening and enrollment process for a phase I vaccine trial in Masaka, Uganda that investigated the safety and immunogenicity of a self-amplifying SARS-CoV-2 RNA vaccine amongst individuals with and without antibodies to SARS-CoV-2. Participant screening and enrollment were conducted between December 2021 and April 2022. Individuals were eligible if they were aged between 18 and 45 years, healthy, and never vaccinated against COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 antibody status was determined using two point-of-care rapid tests, i.e. Multi G (MGFT3) and Standard Q (Standard Q COVID-19 IgM/IgG Plus). Data were entered and managed in OpenClinica. Analyses were performed and presented descriptively. A total of 212 individuals were screened and 43(20.3%) enrolled. The most common reasons for exclusion were ≥ grade 1 laboratory abnormalities (39, 18.4%), followed by discordant SARS-CoV-2 antibody results (23, 10.9%). While the first 38 participants were quickly enrolled over a period of 9 weeks, it took another 9 weeks to enroll the remaining five, as antibody negative participants became scarce during the surge of the Omicron variant. The SARS-CoV-2 antibody positivity rate was determined to be 60.8% and 84.4% in each half of the 18 months of screening respectively. The mean age (±Standard Deviation, SD) of screened and enrolled participants was 27.7 (±8.1) and 30.2 (±8.3) years respectively. We demonstrated that it is feasible to successfully screen and enroll participants for COVID-19 vaccine trials in Uganda in the time of a pandemic. Our experiences may be useful for investigators planning to undertake similar work in Africa.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; enrolment; screening; self-amplifying RNA; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Korang SK, von Rohden E, Veroniki AA, Ong G, Ngalamika O, Siddiqui F, Juul S, Nielsen EE, Feinberg JB, Petersen JJ, et al. Vaccines to prevent COVID-19: a living systematic review with trial sequential analysis and network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0260733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260733. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bekker L-G, Garrett N, Goga A, Fairall L, Reddy T, Yende-Zuma N, Kassanjee R, Collie S, Sanne I, Boulle A, et al. Effectiveness of the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine in health-care workers in South Africa (the Sisonke study): results from a single-arm, open-label, phase 3B, implementation study. Lancet. 2022;399(10330):1141–53. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00007-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
