De novo network analysis reveals autism causal genes and developmental links to co-occurring traits
- PMID: 37553252
- PMCID: PMC10410065
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202302142
De novo network analysis reveals autism causal genes and developmental links to co-occurring traits
Abstract
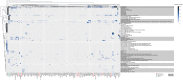
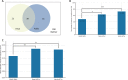
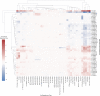
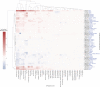
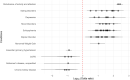
Autism is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that manifests in various ways. Autism is often accompanied by other conditions, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and schizophrenia, which can complicate diagnosis and management. Although research has investigated the role of specific genes in autism, their relationship with co-occurring traits is not fully understood. To address this, we conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomisation analysis and identified four genes located at the 17q21.31 locus that are putatively causal for autism in fetal cortical tissue (LINC02210, LRRC37A4P, RP11-259G18.1, and RP11-798G7.6). LINC02210 was also identified as putatively causal for autism in adult cortical tissue. By integrating data from expression quantitative trait loci, genes and protein interactions, we identified that the 17q21.31 locus contributes to the intersection between autism and other neurological traits in fetal cortical tissue. We also identified a distinct cluster of co-occurring traits, including cognition and worry, linked to the genetic loci at 3p21.1. Our findings provide insights into the relationship between autism and co-occurring traits, which could be used to develop predictive models for more accurate diagnosis and better clinical management.
© 2023 Miller et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5 (R)). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- Antaki D, Guevara J, Maihofer AX, Klein M, Gujral M, Grove J, Carey CE, Hong O, Arranz MJ, Hervas A, et al. (2022) A phenotypic spectrum of autism is attributable to the combined effects of rare variants, polygenic risk and sex. Nat Genet 54: 1284–1292. 10.1038/s41588-022-01064-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Autism Spectrum Disorders Working Group of The Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (2017) Meta-analysis of GWAS of over 16,000 individuals with autism spectrum disorder highlights a novel locus at 10q24.32 and a significant overlap with schizophrenia. Mol Autism 8: 21. 10.1186/s13229-017-0137-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
