MedalCare-XL: 16,900 healthy and pathological synthetic 12 lead ECGs from electrophysiological simulations
- PMID: 37553349
- PMCID: PMC10409805
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-023-02416-4
MedalCare-XL: 16,900 healthy and pathological synthetic 12 lead ECGs from electrophysiological simulations
Abstract
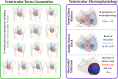
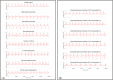
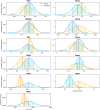
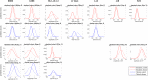
Mechanistic cardiac electrophysiology models allow for personalized simulations of the electrical activity in the heart and the ensuing electrocardiogram (ECG) on the body surface. As such, synthetic signals possess known ground truth labels of the underlying disease and can be employed for validation of machine learning ECG analysis tools in addition to clinical signals. Recently, synthetic ECGs were used to enrich sparse clinical data or even replace them completely during training leading to improved performance on real-world clinical test data. We thus generated a novel synthetic database comprising a total of 16,900 12 lead ECGs based on electrophysiological simulations equally distributed into healthy control and 7 pathology classes. The pathological case of myocardial infraction had 6 sub-classes. A comparison of extracted features between the virtual cohort and a publicly available clinical ECG database demonstrated that the synthetic signals represent clinical ECGs for healthy and pathological subpopulations with high fidelity. The ECG database is split into training, validation, and test folds for development and objective assessment of novel machine learning algorithms.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


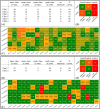
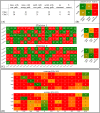
References
-
- Roberts M, et al. Common pitfalls and recommendations for using machine learning to detect and prognosticate for COVID-19 using chest radiographs and CT scans. Nature Machine Intelligence. 2021;3:199–217. doi: 10.1038/s42256-021-00307-0. - DOI
-
- Puyol-Antón, E. et al. Fairness in cardiac MR image analysis: An investigation of bias due to data imbalance in deep learning based segmentation. In de Bruijne, M. et al. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021, 413–423, 10.1007/978-3-030-87199-4_39 (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MedalCare 18HLT07/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 18HLT07/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 18HLT07/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 18HLT07/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 18HLT07/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 18HLT07/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 18HLT07/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 18HLT07/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- FS/20/26/34952 and RE/18/5/34216/British Heart Foundation (BHF)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

