Understanding the Role of Adipocytes and Fibroblasts in Cancer
- PMID: 37553786
- PMCID: PMC10840614
- DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003658
Understanding the Role of Adipocytes and Fibroblasts in Cancer
Abstract
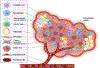
Cancer is currently the second leading cause of death in the United States. There is increasing evidence that the tumor microenvironment (TME) is pivotal for tumorigenesis and metastasis. Recently, adipocytes and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in the TME have been shown to play a major role in tumorigenesis of different cancers, specifically melanoma. Animal studies have shown that CAFs and adipocytes within the TME help tumors evade the immune system, for example, by releasing chemokines to blunt the effectiveness of the host defense. Although studies have identified that adipocytes and CAFs play a role in tumorigenesis, adipocyte transition to fibroblast within the TME is fairly unknown. This review intends to elucidate the potential that adipocytes may have to transition to fibroblasts and, as part of the TME, a critical role that CAFs may play in affecting the growth and invasion of tumor cells. Future studies that illuminate the function of adipocytes and CAFs in the TME may pave way for new antitumor therapies.
Copyright © 2023 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest and sources of funding: none declared. This work was supported by the Hagey Laboratory for Pediatric Regenerative Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Bochet L, Lehuédé C, Dauvillier S, et al. Adipocyte-derived fibroblasts promote tumor progression and contribute to the desmoplastic reaction in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73(18):5657–5668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

