High diagnostic performance of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid beta-synuclein for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- PMID: 37553789
- PMCID: PMC10578883
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51873
High diagnostic performance of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid beta-synuclein for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
Abstract
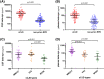
Beta-synuclein is a promising cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarker of synaptic damage. Here we analysed its accuracy in the discrimination between sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (n = 150) and non-prion rapidly progressive dementias (n = 106). In cerebrospinal fluid, beta-synuclein performed better than protein 14-3-3 (AUC 0.95 vs. 0.89) and, to a lesser extent, than total tau (AUC 0.92). Further, the diagnostic value of plasma beta-synuclein (AUC 0.91) outperformed that of plasma tau (AUC 0.79) and neurofilament light chain protein (AUC 0.65) and was comparable to that of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Beta-synuclein might represent the first highly accurate blood biomarker for the diagnosis of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
© 2023 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
M.O. gave scientific advice to Axon, Biogen Idec, Fujirebio and Roche, all unrelated to the work presented in this paper. The foundation of the state Baden–Wuerttemberg handed in a patent for the measurement of β‐synuclein in neurological diseases. Relevant authors are M.O., S.H., and P.O. The other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Parchi P, Giese A, Capellari S, et al. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt‐Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann Neurol. 1999;46(2):224‐233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
