BCR-ABL1-driven exosome-miR130b-3p-mediated gap-junction Cx43 MSC intercellular communications imply therapies of leukemic subclonal evolution
- PMID: 37554265
- PMCID: PMC10405834
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.83178
BCR-ABL1-driven exosome-miR130b-3p-mediated gap-junction Cx43 MSC intercellular communications imply therapies of leukemic subclonal evolution
Abstract
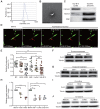
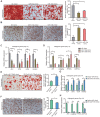
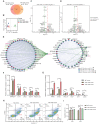
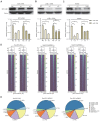
Rationale: In the bone marrow microenvironment (BMME), mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) control the self-renewal of both healthy and cancerous hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs). We previously showed that in vivo leukemia-derived MSCs change neighbor MSCs into leukemia-permissive states and boost leukemia cell proliferation, survival, and chemotherapy resistance. But the mechanisms behind how the state changes are still not fully understood. Methods: Here, we took a reverse engineering approach to determine BCR-ABL1+ leukemia cells activated transcriptional factor C/EBPβ, resulting in miR130a/b-3p production. Then, we back-tracked from clinical specimen transcriptome sequencing to cell co-culture, molecular and cellular assays, flow cytometry, single-cell transcriptome, and transcriptional regulation to determine the molecular mechanisms of BCR-ABL1-driven exosome-miR130b-3p-mediated gap-junction Cx43 MSC intercellular communications. Results: BCR-ABL1-driven exosome-miR130a/b-3p mediated gap-junction Cx43 (a.k.a., GJA1) BMSC intercellular communications for subclonal evolution in leukemic microenvironment by targeting BMSCs-expressed HLAs, thereby potentially maintaining BMSCs with self-renewal properties and reduced BMSC immunogenicity. The Cx43low and miR-130a/bhigh subclonal MSCs subsets of differentiation state could be reversed to Cx43high and miR-130a/blow subclones of the higher stemness state in Cx43-overexpressed subclonal MSCs. Both miR-130a and miR-130b might only inhibit Cx43 translation or degrade Cx43 proteins and did not affect Cx43 mRNA stability. The subclonal evolution was further confirmed by single-cell transcriptome profiling of MSCs, which suggested that Cx43 regulated their stemness and played normal roles in immunomodulation antigen processing. Thus, upregulated miR-130a/b promoted osteogenesis and adipogenesis from BMSCs, thereby decreasing cancer progression. Our clinical data validated that the expression of many genes in human major histocompatibility was negatively associated with the stemness of MSCs, and several immune checkpoint proteins contributing to immune escape in tumors were overexpressed after either miR-130a or miR-130b overexpression, such as CD274, LAG3, PDCD1, and TNFRSF4. Not only did immune response-related cytokine-cytokine receptor interactions and PI3K-AKT pathways, including EGR3, TNFRSF1B, but also NDRG2 leukemic-associated inflammatory factors, such as IFNB1, CXCL1, CXCL10, and CCL7 manifest upon miR-130a/b overexpression. Either BCR siRNAs or ABL1 siRNAs assay showed significantly decreased miR-130a and miR-130b expression, and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing confirmed that the regulation of miR-130a and miR-130b expression is BCR-ABL1-dependent. BCR-ABL1 induces miR-130a/b expression through the upregulation of transcriptional factor C/EBPβ. C/EBPβ could bind directly to the promoter region of miR-130b-3p, not miR-130a-3p. BCR-ABL1-driven exosome-miR130a-3p could interact with Cx43, and further impact GJIC in TME. Conclusion: Our findings shed light on how leukemia BCR-ABL1-driven exosome-miR130b-3p could interact with gap-junction Cx43, and further impact GJIC in TME, implications for leukemic therapies of subclonal evolution.
Keywords: B progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia; BCR-ABL1; Cx43; MSCs; acute lymphoblastic leukemia; chemotherapy resistance; gap junctions; leukemic microenvironment; miR-130a and miR-130b; stemness.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- von Bubnoff N, Schneller F, Peschel C, Duyster J. BCR-ABL gene mutations in relation to clinical resistance of Philadelphia-chromosome-positive leukaemia to STI571: a prospective study. Lancet. 2002;359:487–91. - PubMed
-
- Cheson BD. Clinical advances in hematology & oncology. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2012;10:8. - PubMed
-
- Podvin B, Guermouche H, Roynard P, Goursaud L, Berthon C, Ouafi M. et al. Subclonal acquisition of a BCR::ABL1 fusion in a chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2022;101:2093–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

