Behavioral Analytics for Myopic Agents
- PMID: 37554315
- PMCID: PMC10406492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejor.2023.03.034
Behavioral Analytics for Myopic Agents
Abstract
Many multi-agent systems have a single coordinator providing incentives to a large number of agents. Two challenges faced by the coordinator are a finite budget from which to allocate incentives, and an initial lack of knowledge about the utility function of the agents. Here, we present a behavioral analytics approach for solving the coordinator's problem when the agents make decisions by maximizing utility functions that depend on prior system states, inputs, and other parameters that are initially unknown. Our behavioral analytics framework involves three steps: first, we develop a model that describes the decision-making process of an agent; second, we use data to estimate the model parameters for each agent and predict their future decisions; and third, we use these predictions to optimize a set of incentives that will be provided to each agent. The framework and approaches we propose in this paper can then adapt incentives as new information is collected. Furthermore, we prove that the incentives computed by this approach are asymptotically optimal with respect to a loss function that describes the coordinator's objective. We optimize incentives with a decomposition scheme, where each sub-problem solves the coordinator's problem for a single agent, and the master problem is a pure integer program. We conclude with a simulation study to evaluate the effectiveness of our approach for designing a personalized weight loss program. The results show that our approach maintains efficacy of the program while reducing its costs by up to 60%, while adaptive heuristics provide substantially less savings.
Keywords: Control; Health care; Optimization; Statistical Inference.
Figures


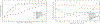
References
-
- Adlakha S, & Johari R (2013). Mean field equilibrium in dynamic games with strategic complementarities. OR, 61, 971–989.
-
- Ahuja R, & Orlin J (2001). Inverse optimization. OR, 49, 771–783.
-
- Astrom K, & Wittenmark B (1995). Adaptive Control. Addison–Wesley.
-
- Aswani A (2019). Statistics with set-valued functions: applications to inverse approximate optimization. Mathematical Programming, 174, 225–251.
-
- Aswani A, Gonzalez H, Sastry S, & Tomlin C (2013). Provably safe and robust learning-based model predictive control. Automatica, 49, 1216–1226.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
