The predictive values of monocyte-lymphocyte ratio in postoperative acute kidney injury and prognosis of patients with Stanford type A aortic dissection
- PMID: 37554321
- PMCID: PMC10404983
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1195421
The predictive values of monocyte-lymphocyte ratio in postoperative acute kidney injury and prognosis of patients with Stanford type A aortic dissection
Abstract
Objectives: Postoperative acute kidney injury (pAKI) is a serious complication of Stanford type A aortic dissection (TAAD) surgery, which is significantly associated with the inflammatory response. This study aimed to explore the relationship between blood count-derived inflammatory markers (BCDIMs) and pAKI and to construct a predictive model for pAKI.
Methods: Patients who underwent TAAD surgery were obtained from our center and the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC)-IV database. The differences in preoperative BCDIMs and clinical outcomes of patients with and without pAKI were analyzed. Logistic regression was used to construct predictive models based on preoperative BCDIMs or white cell counts (WCCs). The performance of the BCDIMs and WCCs models was evaluated and compared using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, area under the ROC curve (AUC), Hosmer-Lemeshow test, calibration plot, net reclassification index (NRI), integrated discrimination improvement index (IDI), and decision curve analysis (DCA). The Kaplan-Meier curves were applied to compare the survival rate between different groups.
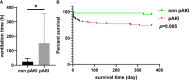
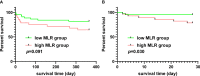
Results: The overall incidence of pAKI in patients who underwent TAAD surgery from our center was 48.63% (124/255). The presence of pAKI was associated with longer ventilation time, higher incidence of cerebral complications and postoperative hepatic dysfunction, and higher in-hospital mortality. The results of the logistic regression indicated that the monocyte-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) was an independent risk factor for pAKI. The BCDIMs model had good discriminating ability, predictive ability, and clinical utility. In addition, the performance of the BCDIMs model was significantly better than that of the WCCs model. Analysis of data from the MIMIC-IV database validated that MLR was an independent risk factor for pAKI and had predictive value for pAKI. Finally, data from the MIMIC-IV database demonstrated that patients with a high MLR had a significantly poor 28-day survival rate when compared to patients with a low MLR.
Conclusion: Our study suggested that the MLR is an independent risk factor for pAKI. A predictive model based on BCDIMs had good discriminating ability, predictive ability, and clinical utility. Moreover, the performance of the BCDIMs model was significantly better than that of the WCCs model. Finally, a high MLR was significantly associated with poor short-term survival of patients who underwent TAAD surgery.
Keywords: monocyte-lymphocyte ratio; postoperative acute kidney injury; predictive model; risk factor; type A aortic dissection.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Dong, Fang, Shi, Luo, Tang and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Howard DP, Banerjee A, Fairhead JF, Perkins J, Silver LE, Rothwell PM, et al. . Population-based study of incidence and outcome of acute aortic dissection and premorbid risk factor control: 10-year results from the Oxford Vascular Study. Circulation (2013) 127(20):2031–7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.000483 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duan WX, Wang WG, Xia L, Xue C, Yu B, Ren K, et al. . Clinical profiles and outcomes of acute type A aortic dissection and intramural hematoma in the current era: lessons from the first registry of aortic dissection in China. Chin Med J (Engl) (2021) 134(8):927–34. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001459 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

