Analyzing the influence of oblique incidence on quantitative backscattering tissue polarimetry: a pilot ex vivo study
- PMID: 37554626
- PMCID: PMC10406390
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.28.10.102905
Analyzing the influence of oblique incidence on quantitative backscattering tissue polarimetry: a pilot ex vivo study
Abstract
Significance: Among the available polarimetric techniques, backscattering Mueller matrix (MM) polarimetry provides a promising non-contact and quantitative tool for in vivo tissue detection and clinical diagnosis. To eliminate the surface reflection from the sample cost-effectively, the non-collinear backscattering MM imaging setup always has an oblique incidence. Meanwhile, for practical organ cavities imaged using polarimetric gastrointestinal endoscopy, the uneven tissue surfaces can induce various relative oblique incidences inevitably, which can affect the polarimetry in a complicated manner and needs to be considered for detailed study.
Aim: The purpose of this study is to systematically analyze the influence of oblique incidence on backscattering tissue polarimetry.
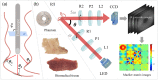
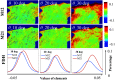
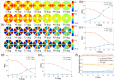
Approach: We measured the MMs of experimental phantom and ex vivo tissues with different incident angles and adopted a Monte Carlo simulation program based on cylindrical scattering model for further verification and analysis. Meanwhile, the results were quantitatively evaluated using the Fourier transform, basic statistics, and frequency distribution histograms.
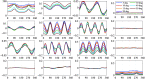
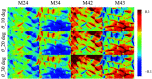
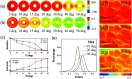
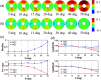
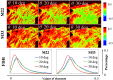
Results: Oblique incidence can induce different changes on non-periodic, two-periodic, and four-periodic MM elements, leading to false-positive and false-negative polarization information for tissue polarimetry. Moreover, a prominent oblique incidence can bring more dramatic signal variations, such as phase retardance and element transposition.
Conclusions: The findings presented in this study give some crucial criterions of appropriate incident angle selections for in vivo polarimetric endoscopy and other applications and can also be valuable references for studying how to minimize the influence further.
Keywords: Monte Carlo simulation; Mueller matrix; endoscopy; polarimetry; scattering imaging.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis and optimization of aberration induced by oblique incidence for in-vivo tissue polarimetry.Opt Lett. 2023 Dec 1;48(23):6136-6139. doi: 10.1364/OL.501365. Opt Lett. 2023. PMID: 38039210
-
Complex Spatial Illumination Scheme Optimization of Backscattering Mueller Matrix Polarimetry for Tissue Imaging and Biosensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 22;14(4):208. doi: 10.3390/bios14040208. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667201 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the Influence of Specular Reflection and Overexposure on Backscattering Mueller Matrix Polarimetry for Tissue Imaging and Sensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 May 21;15(5):333. doi: 10.3390/bios15050333. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422072 Free PMC article.
-
Mueller polarimetric imaging for surgical and diagnostic applications: a review.J Biophotonics. 2017 Aug;10(8):950-982. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201600152. Epub 2017 May 2. J Biophotonics. 2017. PMID: 28464464 Review.
-
Tissue polarimetry: concepts, challenges, applications, and outlook.J Biomed Opt. 2011 Nov;16(11):110801. doi: 10.1117/1.3652896. J Biomed Opt. 2011. PMID: 22112102 Review.
References
-
- Ramella-Roman J. C., Saytashev I., Piccini M., “A review of polarization-based imaging technologies for clinical and preclinical applications,” J. Opt. 22(12), 123001 (2020).10.1088/2040-8986/abbf8a - DOI
-
- He H., et al. , “Mueller matrix polarimetry—an emerging new tool for characterizing the microstructural feature of complex biological specimen,” J. Light. Technol. 37(11), 2534–2548 (2019).JLTEDG10.1109/JLT.2018.2868845 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

