Predictors and a prediction model for positive fine needle aspiration biopsy in C-TIRADS 4 thyroid nodules
- PMID: 37554760
- PMCID: PMC10405816
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1154984
Predictors and a prediction model for positive fine needle aspiration biopsy in C-TIRADS 4 thyroid nodules
Abstract
Objectives: To screen out the predictors and establish a prediction model of positive fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) in the Chinese Guidelines for Malignant Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodule Ultrasound (C-TIRADS) 4 thyroid nodules, and this nomogram can help clinicians evaluate the risk of positive FNAB and determine if FNAB is necessary.
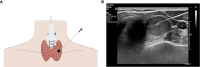
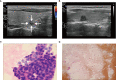
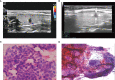
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed data from 547 patients who had C-TIRADS 4 thyroid nodules and underwent fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University between November 30, 2021 and September 5, 2022. Patients who met our inclusion criteria were divided into two groups based on positive or negative FNAB results. We compared their ultrasound (US) features, BRAF V600E status, thyroid function, and other general characteristics using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses to identify independent predictors. These predictors were then used to construct a nomogram. The calibration plot, area under the curve (AUC), and decision curve analysis were employed to evaluate the calibration, discrimination, and clinical utility of the prediction model.
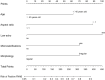
Results: Out of 547 patients, 39.3% (215/547) had a positive result on fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB), while 60.7% (332/547) had a negative result. Univariate logistic regression analysis revealed no significant differences in TPOAb, TgAb, TSH, Tg, nodule location, sex, or solid status between the two groups (P>0.05). However, age, nodule size, internal or surrounding blood flow signal, microcalcifications, aspect ratio, morphology, and low echo showed significant differences (P<0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to explore the correlation between potential independent predictors. The results showed that only age (OR=0.444, 95% Cl=0.296~0.666, P<0.001), low echo (OR=3.549, 95% Cl=2.319~5.432, P<0.001), microcalcifications (OR=2.531, 95% Cl=1.661~3.856, P<0.001), aspect ratio (OR=3.032, 95% Cl=1.819~5.052, P<0.001), and morphology (OR=2.437, 95% Cl=1.586~3.745, P<0.001) were independent predictors for a positive FNAB. These variables were used to construct a prediction nomogram. An ROC curve analysis was performed to assess the accuracy of the nomogram, and AUC=0.793, which indicated good discrimination and decision curve analysis demonstrated clinical significance within a threshold range of 14% to 91%.
Conclusion: In conclusion, 5 independent predictors of positive FNAB, including age (≤45 years old), low echo (yes), microcalcifications (yes), aspect ratio (>1) and morphology (irregular), were identified. A nomogram was established based on the above 5 predictors, and the nomogram can be used as a complementary basis to help clinicians make decisions on FNAB of C-TI-RADS 4 thyroid nodules.
Keywords: 95% Cl=0.296~0.666; C-TIRADS; fine needle aspiration biopsy; low echo (OR=3.549); prediction model 444; predictor; thyroid nodules.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Gao and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that there were no commercial or financial relationships that could potentially create conflicts of interest during the course of this research.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Value of a BRAFV600E and lymphocyte subset-based nomogram for discriminating benign lesions from papillary thyroid carcinoma in C-TIRADS 3 and higher nodules.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Aug 15;16:1608222. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1608222. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40895621 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors and a Prediction Model for Central Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (cN0).Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 27;12:789310. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.789310. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35154002 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Value of the Nomogram Model Based on Multimodal Ultrasound Features for Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules of C-TIRADS Category 4.Ultrason Imaging. 2024 Nov;46(6):320-331. doi: 10.1177/01617346241271184. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Ultrason Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39161273
-
Diagnostic accuracy of palpation versus ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy for diagnosis of malignancy in thyroid nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Jul 17;22(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01085-5. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 35843955 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnostic work-up of euthyroid nodules: which nodules should undergo fine-needle aspiration biopsy? Relevance of ultrasound].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2009 Dec;134(49):2498-503. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1243052. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2009. PMID: 19941231 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Nomogram Model for ACR TI-RADS 4 Nodules Based on Clinical, Biochemical Data and Sonographic Patterns.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2025 Jan;102(1):79-90. doi: 10.1111/cen.15130. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2025. PMID: 39279486 Free PMC article.
-
Do stylet needles improve diagnostic accuracy in thyroid fine-needle aspiration? A retrospective analysis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Jun 9;25(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01971-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 40490730 Free PMC article.
-
XGBoost-based machine learning model combining clinical and ultrasound data for personalized prediction of thyroid nodule malignancy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 29;16:1639639. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1639639. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40801033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pemayun TGD. Current diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules. Acta Med Indones (2016) 48(3):247–57. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins SP, Jamieson SG, Coomarasamy CN, Low IC. The global epidemic of thyroid cancer overdiagnosis illustrated using 18 months of consecutive nodule biopsy correlating clinical priority, ACR-TIRADS and Bethesda scoring. J Med Imag Radiat Oncol (2021) 65(3):309–16. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.13161 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Yang Y, Wu S, Chen K, Luo H, Huang J. Diagnostic performance of US-based FNAB criteria of the 2020 Chinese guideline for malignant thyroid nodules: comparison with the 2017 American College of Radiology guideline, the 2015 American Thyroid Association guideline, and the 2016 Korean Thyroid Association guideline. Quant Imag Med Surg (2021) 11(8):3604–18. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-1365 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

